Chapter 1
第 1 章
Topic: a topic is like a category/an index, it groups messages together.
Topic:主题就像一个类别或索引,它将消息分组在一起。
Producer: processes that push messages to Kafka topics.
Producer:向 Kafka 主题推送消息的进程。
Consumer: processes that consume messages from Kafka topics.
Consumer:从 Kafka 主题消费消息的进程。
Partition: an immutable sequence of topic messages that is continually appended to a structured commit log.
Partition:主题消息的不可变序列,它被不断地追加到结构化的提交日志中。
Kafka broker: one or more servers that form a Kafka cluster.
Kafka broker:组成 Kafka 集群的一台或多台服务器。
Consumer Groups: these are groups of consumers that are used to load share. If a consumer group is consuming messages from one partition, each consumer in a consumer group will consume a different message. Consumer groups are typically used to load share.
Consumer Groups:这是用于负载分担的消费者组。如果一个消费者组正在从一个分区消费消息,该组中的每个消费者将消费不同的消息。消费者组通常用于负载分担。
Queue is a first-in-first-out (FIFO) linear table data structure. You can use an array or a linked list to implement a queue. A queue needs to maintain two pointers, the head points to the head of the queue, and the tail points to the tail of the queue. Move the end of the queue to add elements (enqueue), move the head pointer to delete elements (dequeue).
Queue(队列)是一种先进先出 (FIFO) 的线性表数据结构。你可以使用数组或链表来实现队列。队列需要维护两个指针,头部指向队列的头,尾部指向队列的尾。移动队列的尾部以添加元素(入队),移动头部指针以删除元素(出队)。
Publish/subscribe messaging is a pattern that is characterized by the sender (publisher) of a piece of data (message) not specifically directing it to a receiver.
发布/订阅消息传递是一种模式,其特征在于数据(消息)的发送者(发布者)并不专门将其指向特定的接收者。
The process that pushes the messages to kafka topic is Producer.
将消息推送到 Kafka 主题的进程是 Producer。
Multiple Producers, Multiple Consumers, High Performance makes Kafka a Good Choice over the Traditional Message brokers.
多生产者、多消费者和高性能使得 Kafka 成为优于传统消息代理的不错选择。
Message brokers are used for decoupling data processing from data producers.
消息代理用于将数据处理与数据生产者解耦。
Log Aggregation process of collecting physical log files from servers and putting them in a central place (a file server or HDFS) for processing.
日志聚合是从服务器收集物理日志文件并将其放置在中心位置(文件服务器或 HDFS)进行处理的过程。
Kafka was released as an open-source project on GitHub in 2010.
Kafka 于 2010 年作为开源项目在 GitHub 上发布。
Messages in Kafka are categorized into topics.
Kafka 中的消息被归类为 topics(主题)。
The advanced clients use producers and consumers has building blocks and provide higher-level functionality on top.
高级客户端使用生产者和消费者作为构建块,并在其之上提供更高级的功能。
A key feature of Apache Kafka is that of retention, which is the durable storage of messages for some period of time.
Apache Kafka 的一个关键特性是保留(retention),即消息在一段时间内的持久存储。
Kafka brokers are configured with a default retention setting for topics, either retaining messages for some period of time (e.g., 7 days) or until the topic reaches a certain size in bytes (e.g., 1 GB).
Kafka broker 配置有 topics 的默认保留设置,要么保留消息一段时间(例如 7 天),要么保留直到主题达到特定的大小(例如 1 GB)。
Consumers work as part of a consumer group, which is one or more consumers that work together to consume a topic.
消费者作为 consumer group(消费者组)的一部分工作,消费者组是一个或多个协同工作以消费主题的消费者。
Kafka cluster responds to a rapidly growing large amount of data to scale horizontally. For handling very large message streams Producers can be scaled, Consumers can be scaled, and Brokers can be scaled.
Kafka 集群通过水平扩展来响应快速增长的大量数据。为了处理非常大的消息流,Producers 可以扩展,Consumers 可以扩展,Brokers 也可以扩展。
Apache Kafka provides the circulatory system for the data ecosystem.
Apache Kafka 为数据生态系统提供了循环系统。
Apache Kafka carries messages between the various members of the infrastructure, providing a consistent interface for all clients.
Apache Kafka 在基础设施的各个成员之间传递消息,为所有客户端提供一致的接口。
Consumer Offset is not a component of Kafka.
Consumer Offset(消费者偏移量)不是 Kafka 的组件。
The broker receives messages from producers, assigns offsets to them, and commits the messages to storage on disk.
Broker 接收来自生产者的消息,为它们分配偏移量,并将消息提交到磁盘存储。
In Kafka, producers and consumers are fully decoupled and agnostic of each other.
在 Kafka 中,生产者和消费者是完全解耦的,并且彼此互不知晓。
In Kafka, messages are organized and durably stored in topics.
在 Kafka 中,消息被组织并持久存储在 topics 中。
Topics are partitioned, meaning a topic is spread over a number of “buckets” located on different Kafka brokers.
Topics 是分区的,这意味着一个主题分布在位于不同 Kafka broker 上的多个“桶”中。
Message with the same key are written to the same topic partition.
具有相同键(Key)的消息被写入同一个主题分区。
To make your data fault-tolerant and highly-available, every topic can be replicated.
为了使数据具有容错性和高可用性,每个主题都可以被复制。
Messages and Batches
消息与批次
Kafka supports the compression of batches of messages with an efficient batching format. A batch of messages can be compressed and sent to the server, and this batch of messages is written in compressed form and will remain compressed in the log. The batch will only be decompressed by the consumer.
Kafka 支持使用高效的批处理格式压缩消息批次。一批消息可以被压缩并发送到服务器,这批消息以压缩形式写入,并将保持压缩状态存储在日志中。该批次仅在消费者端解压缩。
Topics and Partitions
主题与分区
Topic groups related events together and durably stores them. The closest analogy for a Kafka topic is a table in a database or folder in a file system.
主题将相关事件分组在一起并持久存储它们。Kafka 主题最接近的类比是数据库中的表或文件系统中的文件夹。
Topics are the central concept in Kafka that decouples producers and consumers. A consumer pulls messages off of a Kafka topic while producers push messages into a Kafka topic. A topic can have many producers and many consumers.
Topics 是 Kafka 中解耦生产者和消费者的核心概念。消费者从 Kafka 主题拉取消息,而生产者将消息推送到 Kafka 主题。一个主题可以有许多生产者和许多消费者。
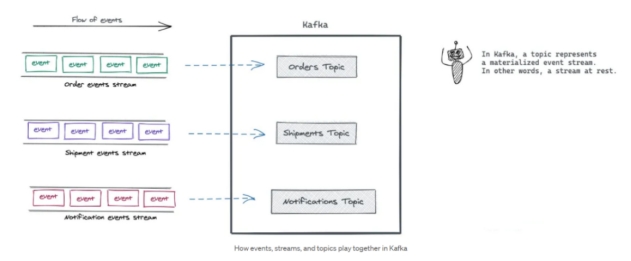
In Kafka, a topic represents a materialized event stream. In other words, a stream at rest.
在 Kafka 中,主题代表具体化的事件流。换句话说,是静态的流。
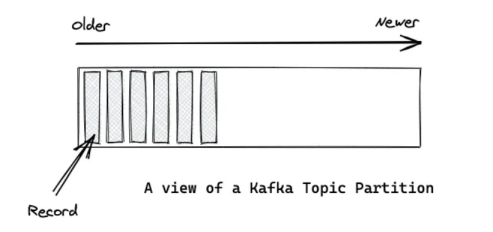
Kafka’s topics are divided into several partitions. While the topic is a logical concept in Kafka, a partition is the smallest storage unit that holds a subset of records owned by a topic. Each partition is a single log file where records are written to it in an append-only fashion.
Kafka 的主题分为几个分区。虽然主题在 Kafka 中是一个逻辑概念,但 partition 是最小的存储单元,保存着主题拥有的一部分记录。每个分区都是一个单独的日志文件,记录以仅追加的方式写入其中。
Producers and Consumers
生产者与消费者
Producers are those client applications that publish (write) events to Kafka, and consumers are those that subscribe to (read and process) these events.
Producers 是那些向 Kafka 发布(写入)事件的客户端应用程序,而 consumers 是那些订阅(读取和处理)这些事件的应用程序。
Brokers and Clusters
Broker 与集群
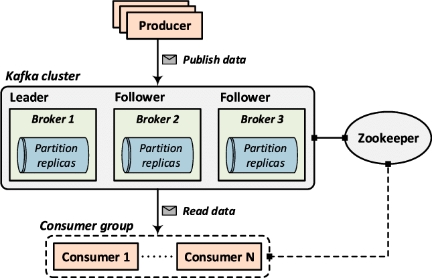
Kafka with more than one broker is called Kafka Cluster. It can be expanded and used without downtime. Apache Kafka Clusters are used to manage the persistence and replication of messages of data, so if the primary cluster goes down, other Kafka Clusters can be used to deliver the same service without any delay.
拥有多个 broker 的 Kafka 称为 Kafka Cluster(集群)。它可以扩展并在不停机的情况下使用。Apache Kafka 集群用于管理数据消息的持久性和复制,因此如果主集群宕机,其他 Kafka 集群可以用于提供相同的服务而没有任何延迟。
Chapter 2
第 2 章
Kafka Console Tool: - Kafka offers command-line tools to manage topics, consumer groups, to consume and publish Messages and so forth.
Kafka 控制台工具:- Kafka 提供命令行工具来管理主题、消费者组,以及消费和发布消息等。
Kafka console scripts are different for Unix-based and Windows platforms.
Kafka 控制台脚本在基于 Unix 和 Windows 的平台上是不同的。
• Apache Kafka uses zookeeper to store metadata about the Kafka cluster.
• Apache Kafka 使用 Zookeeper 来存储关于 Kafka 集群的元数据。
A Kafka broker receives messages from producers and stores them on disk keyed by unique offset.
Kafka 代理(Broker)接收来自生产者的消息,并以唯一的偏移量(offset)为键将其存储在磁盘上。
Every Kafka broker must have an integer identifier, which is set using the broker.id configuration in server.properties.
每个 Kafka 代理必须有一个整数标识符,该标识符在 server.properties 中使用 broker.id 配置进行设置。
num.partitions parameter determines how many partitions a new topic is created with, primarily when automatic topic creation is enabled (which is the default setting).
num.partitions 参数决定了新主题创建时的分区数量,主要用于启用了自动创建主题的情况(这是默认设置)。
Kafka-console-consumer is a consumer command line that: read data from a Kafka topic.
Kafka-console-consumer 是一个消费者命令行工具,用于:从 Kafka 主题读取数据。
When using kafka-console-consumer.sh command, --group option can be used to specify the consumer group ID.
当使用 kafka-console-consumer.sh 命令时,--group 选项可用于指定消费者组 ID。
A Kafka broker receives messages from producer and stores them on disk.
Kafka 代理接收来自生产者的消息并将其存储在磁盘上。
In a kafka cluster, each Kafka broker must have an unique Integer identifier called broker.id.
在 Kafka 集群中,每个 Kafka 代理必须有一个唯一的整数标识符,称为 broker.id。
The total number of bytes of messages retained value is set using the log.retention.bytes parameter.
保留消息的总字节数值是使用 log.retention.bytes 参数设置的。
The metadata for a Kafka broker stores into zookeeper.
Kafka 代理的元数据存储在 Zookeeper 中。
Listeners property we can use in the server.properties file to change the port to the Kafka broker.
我们可以在 server.properties 文件中使用 Listeners 属性来更改 Kafka 代理的端口。
Create Topics.
创建主题。
- To Create Topics, we need to execute commands.
要创建主题,我们需要执行命令。
1 | kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --create --topic myTopic --partitions 1 |
- Now topic is created, we want to check how many topics we have.
现在主题已创建,我们要检查有多少个主题。
1 | kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 -list |
- To see detail information of topics.
查看主题的详细信息。
1 | kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --describe --topic myTopic |
- Delete a topic
删除一个主题
1 | kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic myTopic --delete |
Kafka Cli Producer
Kafka 命令行生产者
This tool is used to write messages to a topic. It is typically not as useful as the console consumer, but it can be useful when the messages are in a text-based format.
该工具用于向主题写入消息。它通常不如控制台消费者有用,但当消息是基于文本的格式时,它会很有用。
- Want to publish some message with the help of producer.
想要借助生产者发布一些消息。
1 | kafka-console-producer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic myTopic |
- Publish message with the help of file.
借助文件发布消息。
1 | kafka-console-producer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic myTopic < file.log |
Kafka Cli Consumer
Kafka 命令行消费者
- Want to subscribe message with the help of consumer.
想要借助消费者订阅消息。
1 | kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic myTopic --from-beginning |
Kafka Cli Consumer Group
Kafka 命令行消费者组
All consumers are part of consumer group. If we do not create group, it will create automatically.
所有消费者都是消费者组的一部分。如果我们不创建组,它会自动创建。
- List of all the consumers which are consuming messages.
列出所有正在消费消息的消费者。
1 | kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 -list |
- To check the description about the consumers
查看关于消费者的描述信息
1 | kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --describe --group console-consumer-46555 |
- To create multiple producers on same node with same topic
在同一节点上为同一主题创建多个生产者
1 | kafka-console-producer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic myTopic |
- To create multiple consumers on same node with same topic
在同一节点上为同一主题创建多个消费者
1 | kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic myTopic |
- check the consumer groups for all consumers using the following command
使用以下命令检查所有消费者的消费者组
1 | kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 -list |
- create a consumer with pre-defined consumer group
创建一个具有预定义消费者组的消费者
1 | kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic myTopic --group myBDGroup |
- read messages from a specific partition
从特定分区读取消息
1 | kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server niit01:9093 --topic b5-topic --partition 0 --from-beginning |
- Produce message with <Key, Value>
生产带有 <Key, Value>(键,值)的消息
1 | kafka-console-producer.sh --bootstrap-server niit01:9093 --property parse.key=true --property key.separator=, --topic test1 |
Eg.-key-1,niit
例如:key-1,niit
- Consumer Message with <Key, Value>
消费带有 <Key, Value>(键,值)的消息
1 | kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server niit01:9092 --property print.key=true --property key.separator="~~" --topic B2-Topic |
Chapter 3
第 3 章
Kafka producers are used to write messages to Kafka.
Kafka 生产者用于向 Kafka 写入消息。
ProducerConfig class helps to set configuration for the Kafka Producer.
ProducerConfig 类有助于设置 Kafka 生产者的配置。
The buffer.memory controls the total amount of memory available to the producer for buffering.
buffer.memory 控制生产者可用于缓冲的总内存量。
Topic, Producer, Consumer are the elements of Kafka.
Topic(主题)、Producer(生产者)、Consumer(消费者)是 Kafka 的要素。
The message is sent and producer waits for acknowledgement of first message to send second message. This message is sent as Synchronously.
消息发送后,生产者等待第一条消息的确认,然后再发送第二条消息。这种消息是同步发送的。
Kafka producer acks property 1 means acknowledgments the producer requires the leader to have received before considering a request complete.
Kafka 生产者的 acks 属性为 1 意味着生产者在认为请求完成之前,需要 Leader 接收到的确认。
Messages read by a Kafka consumer from a topic with multiple partitions are only ordered within single partition.
Kafka 消费者从具有多个分区的 Topic 读取的消息仅在单个分区内有序。
producer.send(record).get() is used to send a message synchronously by using a Kafka producer.
producer.send(record).get() 用于通过 Kafka 生产者同步发送消息。
The send() method is asynchronous.
send() 方法是异步的。
The acks config controls the criteria under which requests are considered complete.
acks 配置控制请求被视为完成的条件。
After creating a KafkaProducer you must close() it to avoid resource leaks.
创建 KafkaProducer 后,必须调用 close() 关闭它以避免资源泄漏。
A Kafka producer is an application that can act as a source of data in a Kafka cluster. A producer can publish messages to one or more Kafka topics.
Kafka 生产者是一个可以充当 Kafka 集群数据源的应用程序。生产者可以将消息发布到一个或多个 Kafka Topic。
Kafka producers send records to topics. The records are sometimes referred to as messages. The producer picks which partition to send a record to per topic. The producer can send records round-robin.
Kafka 生产者将记录发送到 Topic。这些记录有时被称为消息。生产者选择将记录发送到 Topic 的哪个分区。生产者可以轮询发送记录。
We create 3 partition and 3 replications of a topic. Now partitions and replications will save in different broker.
我们创建了一个 Topic 的 3 个分区和 3 个副本。现在分区和副本将保存在不同的 Broker 中。
All the partitions will divide in 3 brokers.
所有分区将分布在 3 个 Broker 中。
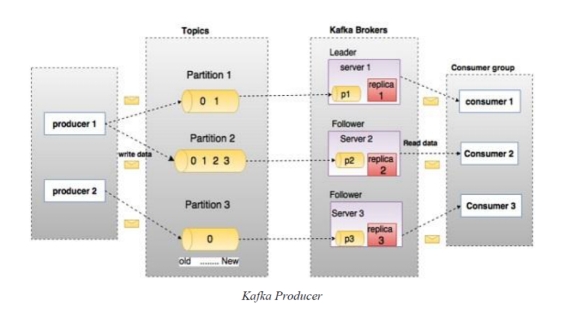
Explanation: - partition 1 is save in broker 1. Partition 2 is saved in broker 2. Partition 3 save in broker 3. (Round Robin Fashion).
解释:分区 1 保存在 Broker 1 中。分区 2 保存在 Broker 2 中。分区 3 保存在 Broker 3 中。(轮询方式)。
We have 2 producers here. Producer 1 produce message in partition 1 and partition 2. Producer 2 producer message in partition 3.
这里有两个生产者。生产者 1 在分区 1 和分区 2 中生成消息。生产者 2 在分区 3 中生成消息。
Overview of Kafka producer Components / Kafka 生产者组件概述
Kafka producer components are as follows:
Kafka 生产者组件如下:
Topic: A topic is a category or feed name to which records are published. Topics in Kafka are always multi-subscriber; that is, a topic can have zero, one, or many consumers that subscribe to the data written to it.
Topic(主题):Topic 是记录发布的类别或提要名称。Kafka 中的 Topic 总是多订阅者的;也就是说,一个 Topic 可以有零个、一个或多个消费者订阅写入其中的数据。
Partition: Kafka topics are divided into a number of partitions. Partitions allow you to parallelize a topic by splitting the data in a particular topic across multiple brokers. Each partition can be placed on a separate machine to allow for multiple consumers to read from a topic in parallel.
Partition(分区):Kafka Topic 被分为若干个分区。分区允许通过将特定 Topic 中的数据拆分到多个 Broker 上来并行化 Topic。每个分区可以放置在单独的机器上,以允许从多个消费者并行读取 Topic。
Serializer: the process of converting an object into a stream of bytes for the purpose of transmission is what we call Serialization. Apache Kafka offers the ability that we can easily publish as well as subscribe to streams of records. Hence, we have the flexibility to create our own custom serializer as well as reserialize which helps to transmit different data type using it.
Serializer(序列化器):将对象转换为字节流以进行传输的过程称为序列化。Apache Kafka 提供了我们可以轻松发布和订阅记录流的能力。因此,我们可以灵活地创建自己的自定义序列化器以及重新序列化,这有助于使用它传输不同的数据类型。
Broker: A broker is a stateless Kafka server. A Kafka cluster is made up of multiple Kafka Brokers. Kafka producer and consumer don’t interact directly but use the Kafka server as an agent or broker to exchange message services. Kafka cluster typically consists of multiple brokers to maintain load balance.
Broker(代理):Broker 是无状态的 Kafka 服务器。Kafka 集群由多个 Kafka Broker 组成。Kafka 生产者和消费者不直接交互,而是使用 Kafka 服务器作为代理或经纪人来交换消息服务。Kafka 集群通常由多个 Broker 组成以维持负载平衡。
Producer API / 生产者 API
We have 2 classes in kafka producer.
Kafka 生产者中有 2 个类。
KafkaProducer - to make producer
KafkaProducer - 用于创建生产者
KafkaRecord - to make the messages
KafkaRecord - 用于创建消息
Properties are an object: With the help of this object, we will set information of bootstrap server address, key serializer, value serializer.
Properties 是一个对象:借助此对象,我们将设置引导服务器地址、键序列化器、值序列化器的信息。
1 | Properties props = new Properties(); |
Bootstrap.servers: A list of host/port pairs to use for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster. The client will make use of all servers irrespective of which servers are specified here for bootstrapping-this list only impacts the initial hosts used to discover the full set of servers.
Bootstrap.servers:用于建立与 Kafka 集群的初始连接的主机/端口对列表。客户端将使用所有服务器,无论此处指定了哪些服务器用于引导——此列表仅影响用于发现完整服务器集的初始主机。
Serializer: - Serialization is the process of converting an object into stream of byte.
Serializer(序列化器):- 序列化是将对象转换为字节流的过程。
key.serializer: - Serializer class for key that implements the org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serializer.
key.serializer:- 实现 org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serializer 的键(key)的序列化器类。
value.serializer: - Serializer class for value that implements the org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serializer.
value.serializer:- 实现 org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serializer 的值(value)的序列化器类。
Kafka Producer / Kafka 生产者
We have to create object for KafkaProducer class.
我们必须为 KafkaProducer 类创建对象。
1 | KafkaProducer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props); |
In this object, we will pass Kafka information.
在这个对象中,我们将传递 Kafka 信息。
1:- Kafka server address.
1:- Kafka 服务器地址。
2: - key serializer.
2:- 键序列化器。
3: - value serializer.
3:- 值序列化器。
KafkaRecord
1 | ProducerRecord<String, String> record = new ProducerRecord<>(topicName, key, value) |
In this object we will pass message information.
在这个对象中,我们将传递消息信息。
1: topic name.
1:Topic 名称。
2: - key
2:- 键(key)
3: - value (message).
3:- 值(消息)。
1 | producer.send(record); |
Chapter 4
第 4 章
Kafka is comparable to traditional messaging systems such as P2P, ActiveMQ.
Kafka 可与传统的各种消息系统(如 P2P、ActiveMQ)相媲美。
Once the consumer subscribes to topics, the poll loop handles all details of A. coordination, B. partition rebalances, C. heartbeats.
一旦消费者订阅了主题,poll 循环就会处理 A. 协调,B. 分区再平衡,C. 心跳的所有细节。
The offsets are committed after the message has been processed. If the processing goes wrong, then the message will be read again by the consumer. It results in duplicate processing of the messages. “At least once” delivery semantics must be used.
偏移量(Offsets)是在消息被处理后提交的。如果处理过程中出现错误,消费者将再次读取该消息。这会导致消息的重复处理。必须使用 “至少一次”(At least once)的交付语义。
Subscribe() method accepts “Single topic name”, “Multiple topic names” and “Regex expression”.
Subscribe() 方法接受 “单主题名称”、”多主题名称” 和 “正则表达式”。
A Consumer Group can be described as a single logical consumer that subscribes to a set of topics which points to application.
消费者组(Consumer Group)可以被描述为一个订阅了一组指向应用程序的主题的单一逻辑消费者。
Kafka stores the offsets at which a consumer group has been reading.
Kafka 存储消费者组读取到的偏移量。
The committed offsets store in a Kafka topic named __consumer_offsets.
已提交的偏移量存储在一个名为 __consumer_offsets 的 Kafka 主题中。
Steps in sequence to read message:
读取消息的顺序步骤:
A. Create consumer properties.
A. 创建消费者属性。
B. Create a consumer.
B. 创建一个消费者。
C. Subscribe the consumer to a specific topic.
C. 将消费者订阅到特定主题。
D. Poll for some new data.
D. 轮询(Poll)一些新数据。
E. Iterate through Consume records.
E. 遍历消费记录。
The group.id property defines a unique identity for the set of consumers within the same consumer group.
group.id 属性为同一消费者组内的一组消费者定义了一个唯一的标识。
The Client.id value is specified by the Kafka consumer client and is used to distinguish between different clients.
Client.id 值由 Kafka 消费者客户端指定,用于区分不同的客户端。
Producer pushes data to Kafka broker then consumer pull data from Kafka broker.
生产者将数据推送到 Kafka 代理(Broker),然后消费者从 Kafka 代理拉取数据。
Consumer client uses the poll method to poll for data from the subscribed topic partition.
消费者客户端使用 poll 方法从订阅的主题分区轮询数据。
The return type of the poll method is ConsumerRecords.
poll 方法的返回类型是 ConsumerRecords。
poll() method will a consumer use to consume records from the subscribed topic by this consumer.
消费者将使用 poll() 方法来消费该消费者订阅的主题中的记录。
In Kafka 2.x, the offset for a topic partition is stored in a Kafka topic.
在 Kafka 2.x 中,主题分区的偏移量存储在 Kafka 主题中。
All consumers that connect to the same Kafka cluster and use the same group.id form a Consumer Group.
连接到同一个 Kafka 集群并使用相同 group.id 的所有消费者组成一个消费者组。
acks is not a Kafka consumer configuration.
acks 不是 Kafka 消费者的配置。
A Kafka consumer is an application that can read data in a Kafka cluster.
Kafka 消费者是一个可以读取 Kafka 集群中数据的应用程序。
A consumer can consume messages from one or more Kafka topics.
一个消费者可以消费一个或多个 Kafka 主题的消息。
Kafka Consumer is used for optimal consumption of Kafka data.
Kafka 消费者用于优化 Kafka 数据的消费。
The primary role of a Kafka consumer is to take Kafka connection and consumer properties to read records from the appropriate Kafka broker.
Kafka 消费者的主要作用是利用 Kafka 连接和消费者属性,从适当的 Kafka 代理读取记录。
Complexities of concurrent application consumption, offset management, delivery semantics, and a lot more are taken care of by Consumer APIs.
并发应用程序消费、偏移量管理、交付语义等许多复杂性都由消费者 API 处理。
These are the steps to create a Kafka consumer:
以下是创建 Kafka 消费者的步骤:
A. Create a Java Class Consumer Demo.java
A. 创建一个 Java 类 Consumer Demo.java
B. Create the consumer properties.
B. 创建消费者属性。
C. Create a consumer.
C. 创建一个消费者。
D. Subscribe the consumer to a specific topic.
D. 将消费者订阅到特定主题。
E. Create a Poll loop to receive data.
E. 创建一个轮询(Poll)循环以接收数据。
Here, we will list the required properties of a consumer:
在这里,我们将列出消费者所需的属性:
key.deserializer: It is a Deserializer class for the key, which is used to implement the org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Deserializer interface.
key.deserializer:这是键(key)的反序列化类,用于实现 org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Deserializer 接口。
value.deserializer: A Deserializer class for value which implements the org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Deserializer interface.
value.deserializer:值的反序列化类,实现了 org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Deserializer 接口。
bootstrap.servers: It is a list of host and port pairs that are used to establish an initial connection with the Kafka cluster.It does not contain the full set of servers that a client requires. Only the servers which are required for bootstrapping are required.
bootstrap.servers:这是一个主机和端口对的列表,用于建立与 Kafka 集群的初始连接。它不包含客户端所需的全部服务器集合。只需要用于引导(bootstrapping)的服务器。
group.id: It is a unique string that identifies the consumer of a consumer group.
group.id:这是一个唯一的字符串,用于标识消费者组中的消费者。
auto.offset.reset: This property is required when no initial offset is present or if the current offset does not exist anymore on the server.
auto.offset.reset:当没有初始偏移量或服务器上不再存在当前偏移量时,需要此属性。
There are the following values used to reset the offset values:
以下用于重置偏移量的值:
earliest: This offset variable automatically resets the value to its earliest offset.
earliest:此偏移量变量自动将值重置为最早的偏移量。
latest: This offset variable reset the offset value to its latest offset.
latest:此偏移量变量将偏移量值重置为最新的偏移量。
none: If no previous offset is found for the previous group, it throws an exception to the consumer.
none:如果未找到前一个组的先前偏移量,则向消费者抛出异常。
Subscribe the consumer to a specific topic
将消费者订阅到特定主题
To read the messages from a topic, we need to connect the consumer to the specified topic.Here, we use Arrays.asList() as it allows our consumer to subscribe to multiple topics.
要从主题读取消息,我们需要将消费者连接到指定的主题。在这里,我们要使用 Arrays.asList(),因为它允许我们的消费者订阅多个主题。
Below code shows the implementation of subscription of the consumer to one topic:
下面的代码展示了消费者订阅一个主题的实现:
1 | consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList(topic)); |
Poll for some new data
轮询一些新数据
The consumer reads data from Kafka through the polling method.
消费者通过轮询方法从 Kafka 读取数据。
The poll method returns the data that hasn’t been fetched yet by the consumer subscribed to the partitions.
poll 方法返回订阅了分区的消费者尚未获取的数据。
The duration of the poll call for example .poll(Duration.ofMillis(100)) is the amount of time to block on this call before returning an empty list in case no data was returned (also called long polling).
轮询调用的持续时间,例如 .poll(Duration.ofMillis(100)),是在没有数据返回的情况下(也称为长轮询),在返回空列表之前此调用阻塞的时间量。
Java Consumers inside a Consumer Group
消费者组内的 Java 消费者
We have seen that consumers can share reads in a Consumer Group in order to scale.We can achieve this using the CLI, and of course using Java.
我们已经看到,消费者可以在消费者组中共享读取操作以进行扩展。我们可以使用 CLI 来实现这一点,当然也可以使用 Java。
Partition Rebalance - Groups
分区再平衡 - 组
Moving partition ownership from one consumer to another is called a rebalance.Rebalances are important because they provide the consumer group with high availability and scalability.
将分区所有权从一个消费者移动到另一个消费者称为再平衡(rebalance)。再平衡非常重要,因为它们为消费者组提供了高可用性和可扩展性。
Currently, we only have one consumer in our group, and therefore that consumer reads from all the topic partitions.
目前,我们的组中只有一个消费者,因此该消费者读取所有主题分区。
Automatic Offset Committing Strategy
自动偏移量提交策略
Using the Kafka Consumer Java API, offsets are committed regularly and automatically in order to enable at-least-once reading scenarios.
使用 Kafka Consumer Java API,偏移量会定期自动提交,以实现至少一次(at-least-once)的读取场景。
You can get a refresher on Consumer Offsets here.
你可以在这里复习消费者偏移量(Consumer Offsets)的相关内容。
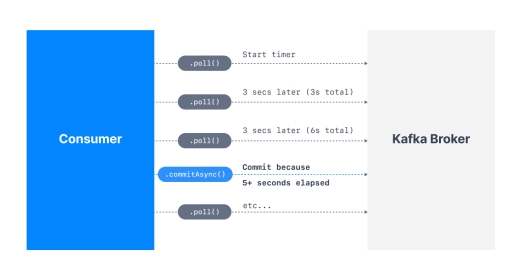
By default, the property enable.auto.commit=true and therefore offsets are committed automatically with a frequency controlled by the config auto.commit.interval.ms.
默认情况下,属性 enable.auto.commit=true,因此偏移量会根据配置 auto.commit.interval.ms 控制的频率自动提交。
The process of committing the offsets happens when the .poll() function is called and the time between two calls to .poll() is greater than the setting auto.commit.interval.ms (5 seconds by default).
提交偏移量的过程发生在调用 .poll() 函数时,并且两次调用 .poll() 之间的时间大于设置 auto.commit.interval.ms(默认为 5 秒)。
This means that to be in an “at-least-once” processing use case (the most desirable one), you need to ensure all the messages in your consumer code are successfully processed before performing another .poll() call.(which is the case in the sample code defined above).If this is not the case, then offsets could be committed before the messages are actually processed, therefore resulting in an “at-most once” processing pattern, possibly resulting in message skipping (which is undesirable).
这意味着要处于 “至少一次” 处理用例(最理想的情况),你需要确保在执行另一次 .poll() 调用之前,消费者代码中的所有消息都已成功处理。(上面定义的示例代码就是这种情况)。如果情况并非如此,那么偏移量可能会在消息实际被处理之前提交,从而导致 “至多一次”(at-most once)的处理模式,可能导致消息跳过(这是不可取的)。
In that (rare) case, you must disable enable.auto.commit, and most likely move processing to a separate thread, and then from time to time call .commitSync() or .commitAsync() with the correct offsets manually.
在这种(罕见)情况下,你必须禁用 enable.auto.commit,并且很可能将处理移动到单独的线程,然后不时手动调用带有正确偏移量的 .commitSync() 或 .commitAsync()。
This complicated use case is discussed in the Kafka Consumer Documentation under the section “Automatic Offset Committing”.
这个复杂的用例在 Kafka 消费者文档的 “Automatic Offset Committing”(自动偏移量提交)部分进行了讨论。
Graceful Shutdown of Consumer (addShutdownHook())
消费者的优雅关闭 (addShutdownHook())
Currently our consumer is running an infinite loop with while(true) but we can catch an Exception that happens when our consumer is shutting down.
目前我们的消费者正在运行一个带有 while(true) 的无限循环,但我们可以捕获消费者关闭时发生的异常。
For this, we need to call consumer.wakeup() which will trigger a WakeupException next time the .poll() function is called.
为此,我们需要调用 consumer.wakeup(),这将在下次调用 .poll() 函数时触发 WakeupException。
The WakeupException itself does not need to be handled, but then in a finally{} block we can call consumer.close() which will take care of:
WakeupException 本身不需要处理,但在 finally{} 块中,我们可以调用 consumer.close(),它将负责:
Committing the offsets if needed.
如果需要,提交偏移量。
Close the connection to Kafka.
关闭与 Kafka 的连接。
In order to call consumer.wakeup() we need to use a ShutdownHook.
为了调用 consumer.wakeup(),我们需要使用 ShutdownHook。
That ShutdownHook needs to be linked to the main thread in order to wait for all threads to complete before shutting down the program.
该 ShutdownHook 需要链接到主线程,以便在关闭程序之前等待所有线程完成。
Kafka Chapter 5
Kafka 第 5 章
Kafka provides a command line utility called bin/kafka-topics.sh to operate topics on the Kafka server.
Kafka 提供了一个名为 bin/kafka-topics.sh 的命令行工具,用于操作 Kafka 服务器上的主题。
The replication factor for a topic controls how many servers will replicate each message that is written.
主题的副本因子(replication factor)控制有多少个服务器将复制写入的每条消息。
The partition count for a topic impacts the maximum parallelism of your consumers.
主题的分区计数(partition count)影响消费者的最大并行度。
To get all available topic names on any Kafka server, use the bin/kafka-topics.sh with --list option.
要在任何 Kafka 服务器上获取所有可用的主题名称,请使用带有 --list 选项的 bin/kafka-topics.sh。
With the bin/kafka-consumer-groups.sh tool, we can operate the consumer groups.
使用 bin/kafka-consumer-groups.sh 工具,我们可以操作消费者组。
To get all the topics that the specified group is consuming as well as the offsets for each topic partition, use the bin/kafka-consumer-groups.sh with --describe and --group option.
要获取指定组正在消费的所有主题以及每个主题分区的偏移量,请使用带有 --describe 和 --group 选项的 bin/kafka-consumer-groups.sh。
The consumer group can be deleted automatically when the last committed offset for that group expires.
当消费者组的最后提交偏移量过期时,该组可以被自动删除。
We can use bin/kafka-consumer-groups.sh to see the consuming position of your consumer.
我们可以使用 bin/kafka-consumer-groups.sh 来查看消费者的消费位置。
To reset offsets of a consumer group with bin/kafka-consumer-groups.sh tool, --reset-offsets option can be used.
要使用 bin/kafka-consumer-groups.sh 工具重置消费者组的偏移量,可以使用 --reset-offsets 选项。
Kafka provides a command line utility called bin/kafka-configs.sh to update some of the broker configs without restarting the broker.
Kafka 提供了一个名为 bin/kafka-configs.sh 的命令行工具,用于在不重启代理(broker)的情况下更新一些代理配置。
For Kafka clients, the only configurations that can be overridden are the producer and consumer quotas.
对于 Kafka 客户端,唯一可以覆盖的配置是生产者和消费者配额。
Monitoring Kafka includes Monitoring Server Stats, Monitoring Producer Stats and Monitoring Consumer Stats.
监控 Kafka 包括监控服务器统计信息、监控生产者统计信息和监控消费者统计信息。
By default, Apache Kafka disables remote JMX.
默认情况下,Apache Kafka 禁用远程 JMX。
We can increase the Kafka topic partition number to a number that is greater than the broker number in the cluster.
我们可以将 Kafka 主题分区数增加到大于集群中代理(broker)数量的数值。
To reset offsets of a consumer group, we can use bin/kafka-consumer-groups.sh utility.
要重置消费者组的偏移量,我们可以使用 bin/kafka-consumer-groups.sh 工具。
If you have three brokers in a cluster, and you specify a producer quota of 10 MB/sec for a client, that client will be allowed to produce 10 MB/sec on each broker at the same time for a total of 30 MB/sec.
如果你在集群中有三个代理,并且为客户端指定了 10 MB/秒的生产者配额,那么该客户端将被允许同时在每个代理上生产 10 MB/秒的数据,总计 30 MB/秒。
To delete a configuration override using bin/kafka-configs.sh, use the --alter command along with the --delete-config parameter.
要使用 bin/kafka-configs.sh 删除配置覆盖,请使用 --alter 命令以及 --delete-config 参数。
Alter Topic
修改主题
- Create a new topic to alter it.
- 创建一个新主题以对其进行修改。
1 | kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9093,localhost:9094,localhost:9095 --create-topic test-topic --partitions 1 --replication-factor 1 |
- Now describe the topic.
- 现在描述该主题。
1 | kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9093 --describe --topic test-topic |
- Now alter the topic.
- 现在修改该主题。
1 | kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9093 --alter --topic test-topic --partitions 2 |
- Describe the topic again to check.
- 再次描述该主题以进行检查。
1 | kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9093 --describe --topic test-topic |
- Delete a topic.
- 删除一个主题。
1 | kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server niit01:9092 --delete --topic B3-topic |
Change Brokers
变更代理
- Generate.
- 生成配置。
1 | kafka-reassign-partitions.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9093 --topics-to-move-json-file /training/topics-to-move.json --broker-list "2,3" --generate |
- JSON file structure -
topics-to-move.json- JSON 文件结构 -
topics-to-move.json
- JSON 文件结构 -
1 | {"topics":[{"topic": "myTopic"}], "version":1} |
- Copy the proposed partition reassignment configuration and create a new json file and remove ,”log_dirs”:[“any”] and save the file with name “suggested-change.json”.
- 复制建议的分区重分配配置,创建一个新的 JSON 文件,删除 ,”log_dirs”:[“any”],并将文件保存为 “suggested-change.json”。
1 | {"version":1,"partitions":[{"topic":"test-topic","partition":0,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"test-topic","partition":1,"replicas":[3]}]} |
- Execute.
- 执行。
1 | kafka-reassign-partitions.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9093 --reassignment-json-file /training/suggested-change.json --execute |
- Verify.
- 验证。
1 | kafka-reassign-partitions.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9093 --reassignment-json-file /training/suggested-change.json --verify |
- Describe the topic to check the status.
- 描述主题以检查状态。
1 | kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9093 --describe --topic test-topic |
Kafka provides several command-line utilities, we can use them to easily make changes to the kafka clusters.
Kafka 提供了几个命令行实用程序,我们可以使用它们轻松地更改 Kafka 集群。
Consumer Operation
消费者操作
With the ConsumerGroup Command tool, we can list, describe, or delete the consumer groups.
使用 ConsumerGroup 命令工具,我们可以列出、描述或删除消费者组。
The consumer group can be deleted manually, or automatically when the last committed offset for that group expires.
消费者组可以手动删除,也可以在该组的最后提交偏移量过期时自动删除。
Manual deletion works only if the group does not have any active members.
手动删除仅在该组没有任何活跃成员时才有效。
List and Describe Groups
列出和描述组
- List of all the consumers which are consuming messages.
- 列出所有正在消费消息的消费者。
1 | kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --list |
- To check the description about the consumers.
- 查看关于消费者的描述。
1 | kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --describe --group console-consumer-46555 |
Delete Group
删除组
1 | kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --delete --group my-group --group my-other-group |
Overriding Topic Configuration Defaults
覆盖主题配置默认值
1 | kafka-configs.sh --bootstrap-server niit:9092 --alter --entity-type topics --entity-name b1-ch5 --add-config retention.ms=3600000 |
Describing Configuration Overrides
描述配置覆盖
1 | kafka-configs.sh --bootstrap-server niit:9092 --describe --entity-type topics --entity-name b5-ch5 |
Removing Configuration Overrides
移除配置覆盖
1 | kafka-configs.sh --bootstrap-server niit:9092 --alter --entity-type topics --entity-name b5-ch5 --delete-config retention.ms |
Monitoring Kafka
监控 Kafka
Kafka uses Yammer Metrics for metrics reporting in both the server and the client.
Kafka 在服务器和客户端中都使用 Yammer Metrics 进行指标报告。
The easiest way to see the available metrics is to fire up JConsole and point it at a running kafka client or server; this will allow browsing all metrics with JMX.
查看可用指标的最简单方法是启动 JConsole 并将其指向正在运行的 Kafka 客户端或服务器;这将允许通过 JMX 浏览所有指标。
JConsole is based on JMX (Java Management Extensions), Apache Kafka disables remote JMX by default.
JConsole 基于 JMX(Java 管理扩展),Apache Kafka 默认禁用远程 JMX。
You can enable remote monitoring using JMX by setting the environment variable JMX_PORT for processes started using the CLI or standard Java system properties to enable remote JMX programmatically.
您可以通过为使用 CLI 启动的进程设置环境变量 JMX_PORT 来启用使用 JMX 的远程监控,或者使用标准 Java 系统属性以编程方式启用远程 JMX。
For example, you can set JMX_PORT when start kafka:
例如,您可以在启动 Kafka 时设置 JMX_PORT:
JMX_PORT=9988 bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties
What is JConsole?
什么是 JConsole?
JConsole (Java™ Monitoring and Management Console) is a graphical tool that allows the user to monitor and manage the behavior of Java applications.
JConsole(Java™ 监控和管理控制台)是一个图形工具,允许用户监控和管理 Java 应用程序的行为。
The JConsole tool is built on the java.lang.management API.
JConsole 工具构建在 java.lang.management API 之上。
JConsole connects to applications that run on the same workstation or on a remote workstation.
JConsole 连接到运行在同一工作站或远程工作站上的应用程序。
The applications must be configured to allow access.
应用程序必须配置为允许访问。
When JConsole connects to a Java application, it reports information about the application.
当 JConsole 连接到 Java 应用程序时,它会报告有关该应用程序的信息。
The details include memory usage, the running threads, and the loaded classes.
详细信息包括内存使用情况、运行的线程和已加载的类。
This data helps you monitor the behavior of your application and the JVM.
这些数据有助于您监控应用程序和 JVM 的行为。
The information is useful in understanding performance problems, memory usage issues, hangs, or deadlocks.
这些信息对于理解性能问题、内存使用问题、挂起或死锁非常有用。
JConsole is a tool in JAVA_HOME/bin for monitoring the status of running Java Programs.
JConsole 是 JAVA_HOME/bin 中的一个工具,用于监控正在运行的 Java 程序的状。
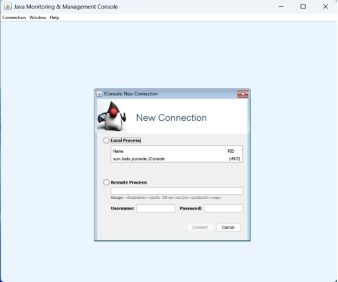
Select remote process, fill host_name/port_number niit(your_hostname):9988 (port or port number on which you enabled JMX) and user and password for the remote system, then click connect.
选择远程进程,填写 host_name/port_number 例如 niit(your_hostname):9988(即您启用 JMX 的端口号)以及远程系统的用户名和密码,然后点击连接。
Chapter 6
第 6 章
Stream is an abstraction representing an unbounded dataset. Unbounded means infinite and ever growing.
流(Stream)是一个代表无界数据集的抽象。无界意味着无限且不断增长。
Event streams are ordered, each event is immutable in event streams and Event streams are replayable.
事件流是有序的,事件流中的每个事件都是不可变的,并且事件流是可重放的。
In Kafka Stream processing concepts, common notions of time include LogAppend Time, Event Time and Processing Time.
在 Kafka 流处理概念中,常见的时间概念包括日志追加时间(LogAppend Time)、事件时间(Event Time)和处理时间(Processing Time)。
State that is maintained in an external datastore, often a NoSQL system like Cassandra is External State.
维护在外部数据存储(通常是像 Cassandra 这样的 NoSQL 系统)中的状态是外部状态。
An example is an app that reads log messages from a stream and writes ERROR events into a high-priority stream and the rest of the events into a low-priority stream.
一个例子是,一个应用程序从流中读取日志消息,将 ERROR 事件写入高优先级流,将其余事件写入低优先级流。
The given Example refers to Single-Event Processing.
给定的例子指的是单事件处理(Single-Event Processing)。
Every stream application implements and executes at least one topology.
每个流应用程序都实现并执行至少一个拓扑。
Kafka Streams scales by allowing multiple threads of executions within one instance of the application and by supporting load balancing between distributed instances of the application.
Kafka Streams 通过允许在一个应用程序实例中执行多个线程,并支持在应用程序的分布式实例之间进行负载均衡来进行扩展。
Kafka Stream use case includes Game real-time rendering.
Kafka Stream 的用例包括游戏实时渲染。
The Streams engine parallelizes execution of a topology by splitting it into Tasks.
Streams 引擎通过将拓扑拆分为任务(Tasks)来并行执行拓扑。
Producer processes the push message to Kafka topics.
生产者处理推送到 Kafka 主题的消息。
A Kafka Partitioner is used to make sure that all events with the same stock symbol are written to the same partition.
Kafka 分区器(Partitioner)用于确保具有相同股票代码的所有事件都被写入同一个分区。
StreamsConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG specifies a list of host/port pairs to use for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster.
StreamsConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG 指定用于建立与 Kafka 集群初始连接的主机/端口对列表。
We can use StreamsBuilder to construct a topology for Kafka streaming processing.
我们可以使用 StreamsBuilder 为 Kafka 流处理构建拓扑。
Most operations on Kafka streams are windowed operation which are operating on slices of time like top products sold this week.
Kafka 流上的大多数操作都是窗口操作,这些操作在时间片段上运行,例如本周销售的热门产品。
A stream can be considered a state changelog of a table.
流可以被看作是表的状变更日志。
A source processor is a special type of stream processor that does not have any upstream processors.
源处理器(Source Processor)是一种特殊类型的流处理器,它没有任何上游处理器。
It produces an input stream to its topology from one or multiple Kafka topics by consuming records from these topics and forwarding them to its down-stream processors.
它通过从一个或多个 Kafka 主题消费记录并将其转发给下游处理器,从而为其拓扑生成输入流。
A sink processor is a special type of stream processor that does not have down-stream processors.
汇处理器(Sink Processor)是一种特殊类型的流处理器,它没有下游处理器。
It sends any received records from its up-stream processors to a specified Kafka topic.
它将从上游处理器接收到的任何记录发送到指定的 Kafka 主题。
start() method can start KafkaStreams instance by starting all its threads, and close() method can shutdown the instance by signaling all the threads to stop.
start() 方法可以通过启动所有线程来启动 KafkaStreams 实例,而 close() 方法可以通过向所有线程发送停止信号来关闭实例。
Kafka Streams is a library for building streaming applications, specifically applications that transform input Kafka topics into output Kafka topics (or call to external services, updates to databases, etc).
Kafka Streams 是一个用于构建流应用程序的库,特别是将输入 Kafka 主题转换为输出 Kafka 主题(或调用外部服务、更新数据库等)的应用程序。
You can see this in the following image:
你可以在接下来的图片中看他:
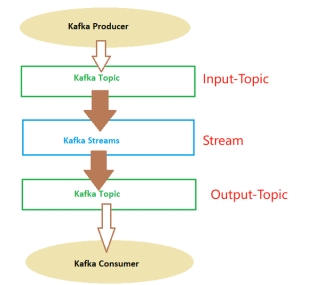
Kafka Streams are applications written in Java or Scala which read continuously from one or more topics and do things.
Kafka Streams 是用 Java 或 Scala 编写的应用程序,它们连续地从一个或多个主题读取并执行操作。
These applications work with some kinds of internal topics named streams.
这些应用程序使用某种名为流的内部主题。
These streams create what the concept named “Kafka Topology”.
这些流创建了名为 “Kafka 拓扑” 的概念。
The Kafka Streams, as you can see in the picture, read data from a topic, filter, aggregate, modify, add data to the messages received from one or more topics and then, generally put that data on another topic.
如图所示,Kafka Streams 从主题读取数据,过滤、聚合、修改、向从一个或多个主题接收的消息添加数据,然后通常将该数据放入另一个主题。
KStream & KTable
KStream 与 KTable
KStream: It represents an unbounded, continuously updating stream of records.
KStream:它代表一个无界的、不断更新的记录流。
Each record in a KStream consists of a key, a value, and a timestamp.
KStream 中的每条记录由键、值和时间戳组成。
KStream can have multiple records with the same key, and new records can be continuously appended to the stream.
KStream 可以有多条具有相同键的记录,并且新记录可以不断追加到流中。
KTable: It represents a changelog stream of records that are organized as a table.
KTable:它代表组织成表的记录变更日志流。
Each record in a KTable has a unique key and a value.
KTable 中的每条记录都有唯一的键和值。
Unlike KStream, KTable maintains the latest value for each key and updates the table with new records.
与 KStream 不同,KTable 维护每个键的最新值,并使用新记录更新表。
It can be seen as a materialized view of the underlying stream.
它可以被视为底层流的物化视图。
Understanding the Topology
理解拓扑
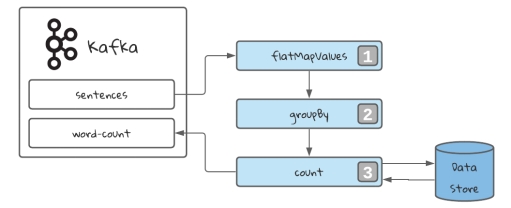
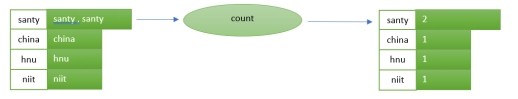
For the above implementation, the input is “Santy china hnu niit santy”.
对于上述实现,输入是 “Santy china hnu niit santy”。
mapValues: Takes one record and produces one record, while retaining the key of the original record.
mapValues:获取一条记录并生成一条记录,同时保留原始记录的键。

flatMapValues: Takes one record and produces zero, one, or more records, while retaining the key of the original record.
flatMapValues:获取一条记录并生成零条、一条或多条记录,同时保留原始记录的键。
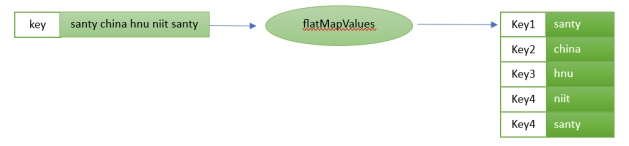
selectKey: Assigns a new key - possibly of a new key type - to each record.
selectKey:为每条记录分配一个新键(可能是新键类型)。
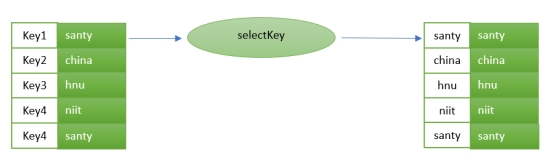
groupByKey: Groups the records by the existing key.
groupByKey:按现有键对记录进行分组。
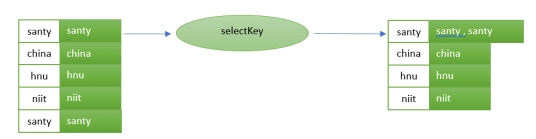
The stream selecting a grouping key. In our case, the word.
流选择一个分组键。在我们的例子中,就是单词。
This will always return grouped stream, prepared to be aggregated.
这将始终返回分组流,准备好进行聚合。
It will also trigger an operation called repartition.
它还将触发一个名为重分区(repartition)的操作。
count: Counts the number of records by the grouped key.
count:按分组键统计记录数。
Count every appearance of the key in the stream. This will be stored in a data store.
计算流中键的每次出现。这将存储在数据存储中。