Chapter 6
第 6 章
Stream is an abstraction representing an unbounded dataset. Unbounded means infinite and ever growing.
流(Stream)是一个代表无界数据集的抽象。无界意味着无限且不断增长。
Event streams are ordered, each event is immutable in event streams and Event streams are replayable.
事件流是有序的,事件流中的每个事件都是不可变的,并且事件流是可重放的。
In Kafka Stream processing concepts, common notions of time include LogAppend Time, Event Time and Processing Time.
在 Kafka 流处理概念中,常见的时间概念包括日志追加时间(LogAppend Time)、事件时间(Event Time)和处理时间(Processing Time)。
State that is maintained in an external datastore, often a NoSQL system like Cassandra is External State.
维护在外部数据存储(通常是像 Cassandra 这样的 NoSQL 系统)中的状态是外部状态。
An example is an app that reads log messages from a stream and writes ERROR events into a high-priority stream and the rest of the events into a low-priority stream. The given Example refers to Single-Event Processing.
一个例子是,一个应用程序从流中读取日志消息,将 ERROR 事件写入高优先级流,将其余事件写入低优先级流。给定的例子指的是单事件处理(Single-Event Processing)。
Every stream application implements and executes at least one topology.
每个流应用程序都实现并执行至少一个拓扑。
Kafka Streams scales by allowing multiple threads of executions within one instance of the application and by supporting load balancing between distributed instances of the application.
Kafka Streams 通过允许在一个应用程序实例中执行多个线程,并支持在应用程序的分布式实例之间进行负载均衡来进行扩展。
Kafka Stream use case includes Game real-time rendering.
Kafka Stream 的用例包括游戏实时渲染。
The Streams engine parallelizes execution of a topology by splitting it into Tasks.
Streams 引擎通过将拓扑拆分为任务(Tasks)来并行执行拓扑。
Producer processes the push message to Kafka topics.
生产者处理推送到 Kafka 主题的消息。
A Kafka Partitioner is used to make sure that all events with the same stock symbol are written to the same partition.
Kafka 分区器(Partitioner)用于确保具有相同股票代码的所有事件都被写入同一个分区。
StreamsConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG specifies a list of host/port pairs to use for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster.
StreamsConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG 指定用于建立与 Kafka 集群初始连接的主机/端口对列表。
We can use StreamsBuilder to construct a topology for Kafka streaming processing.
我们可以使用 StreamsBuilder 为 Kafka 流处理构建拓扑。
Most operations on Kafka streams are windowed operation which are operating on slices of time like top products sold this week.
Kafka 流上的大多数操作都是窗口操作,这些操作在时间片段上运行,例如本周销售的热门产品。
A stream can be considered a state changelog of a table.
流可以被看作是表的状变更日志。
A source processor is a special type of stream processor that does not have any upstream processors.
源处理器(Source Processor)是一种特殊类型的流处理器,它没有任何上游处理器。
It produces an input stream to its topology from one or multiple Kafka topics by consuming records from these topics and forwarding them to its down-stream processors.
它通过从一个或多个 Kafka 主题消费记录并将其转发给下游处理器,从而为其拓扑生成输入流。
A sink processor is a special type of stream processor that does not have down-stream processors.
汇处理器(Sink Processor)是一种特殊类型的流处理器,它没有下游处理器。
It sends any received records from its up-stream processors to a specified Kafka topic.
它将从上游处理器接收到的任何记录发送到指定的 Kafka 主题。
start() method can start KafkaStreams instance by starting all its threads, and close() method can shutdown the instance by signaling all the threads to stop.
start() 方法可以通过启动所有线程来启动 KafkaStreams 实例,而 close() 方法可以通过向所有线程发送停止信号来关闭实例。
Kafka Streams is a library for building streaming applications, specifically applications that transform input Kafka topics into output Kafka topics (or call to external services, updates to databases, etc).
Kafka Streams 是一个用于构建流应用程序的库,特别是将输入 Kafka 主题转换为输出 Kafka 主题(或调用外部服务、更新数据库等)的应用程序。
You can see this in the following image:
你可以在接下来的图片中看他:
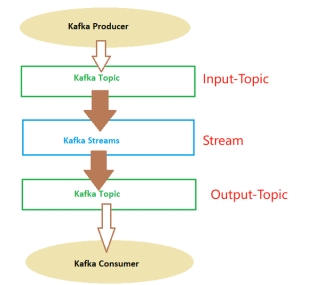
Kafka Streams are applications written in Java or Scala which read continuously from one or more topics and do things.
Kafka Streams 是用 Java 或 Scala 编写的应用程序,它们连续地从一个或多个主题读取并执行操作。
These applications work with some kinds of internal topics named streams.
这些应用程序使用某种名为流的内部主题。
These streams create what the concept named “Kafka Topology”.
这些流创建了名为 “Kafka 拓扑” 的概念。
The Kafka Streams, as you can see in the picture, read data from a topic, filter, aggregate, modify, add data to the messages received from one or more topics and then, generally put that data on another topic.
如图所示,Kafka Streams 从主题读取数据,过滤、聚合、修改、向从一个或多个主题接收的消息添加数据,然后通常将该数据放入另一个主题。
KStream & KTable
KStream 与 KTable
KStream: It represents an unbounded, continuously updating stream of records. Each record in a KStream consists of a key, a value, and a timestamp. KStream can have multiple records with the same key, and new records can be continuously appended to the stream.
KStream:它代表一个无界的、不断更新的记录流。KStream 中的每条记录由键、值和时间戳组成。KStream 可以有多条具有相同键的记录,并且新记录可以不断追加到流中。
KTable: It represents a changelog stream of records that are organized as a table. Each record in a KTable has a unique key and a value. Unlike KStream, KTable maintains the latest value for each key and updates the table with new records. It can be seen as a materialized view of the underlying stream.
KTable:它代表组织成表的记录变更日志流。KTable 中的每条记录都有唯一的键和值。与 KStream 不同,KTable 维护每个键的最新值,并使用新记录更新表。它可以被视为底层流的物化视图。
Understanding the Topology
理解拓扑
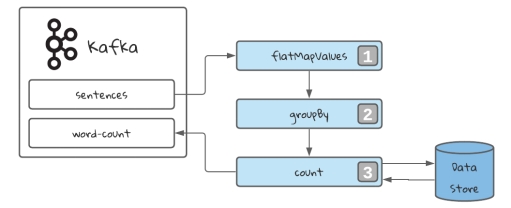
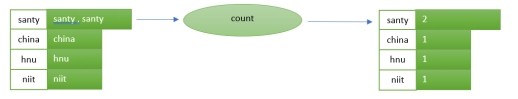
For the above implementation, the input is “Santy china hnu niit santy”.
对于上述实现,输入是 “Santy china hnu niit santy”。
mapValues: Takes one record and produces one record, while retaining the key of the original record.
mapValues:获取一条记录并生成一条记录,同时保留原始记录的键。

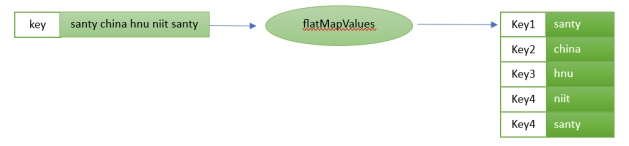
flatMapValues: Takes one record and produces zero, one, or more records, while retaining the key of the original record.
flatMapValues:获取一条记录并生成零条、一条或多条记录,同时保留原始记录的键。
selectKey: Assigns a new key - possibly of a new key type - to each record.
selectKey:为每条记录分配一个新键(可能是新键类型)。
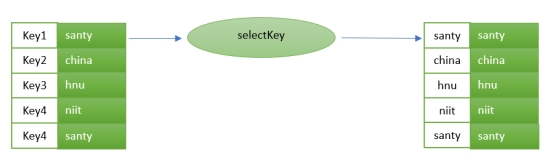
groupByKey: Groups the records by the existing key.
groupByKey:按现有键对记录进行分组。
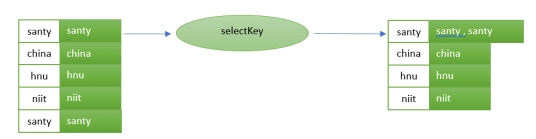
The stream selecting a grouping key. In our case, the word.
流选择一个分组键。在我们的例子中,就是单词。
This will always return grouped stream, prepared to be aggregated.
这将始终返回分组流,准备好进行聚合。
It will also trigger an operation called repartition.
它还将触发一个名为重分区(repartition)的操作。
count: Counts the number of records by the grouped key.
count:按分组键统计记录数。
Count every appearance of the key in the stream. This will be stored in a data store.
计算流中键的每次出现。这将存储在数据存储中。