Chapter 8
第8章
Machine learning, a branch of Artificial Intelligence, is dedicated to creating models and algorithms that enable computers to learn from data and improve based on previous experiences without being explicitly programmed for each specific task.
机器学习是人工智能的一个分支,致力于创建模型和算法,使计算机能够从数据中学习并根据以往的经验进行改进,而无需针对每个具体任务进行显式编程。
Types of Machine learning:
机器学习的类型:
- Supervised Learning 监督学习
- Unsupervised Learning 无监督学习
Supervised Learning
监督学习
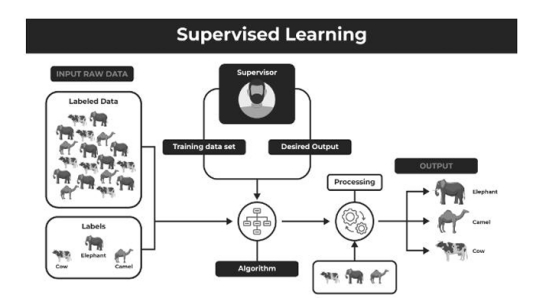
Supervised learning is a machine learning approach where a model is trained on a labeled dataset, meaning that each data point is paired with a corresponding output label. These labeled datasets contain both input features and the associated output values, allowing the algorithm to learn the relationship between them.
监督学习是一种机器学习方法,其中模型是在标记的数据集上训练的,这意味着每个数据点都配对了一个相应的输出标签。这些标记的数据集包含输入特征和关联的输出值,允许算法学习它们之间的关系。
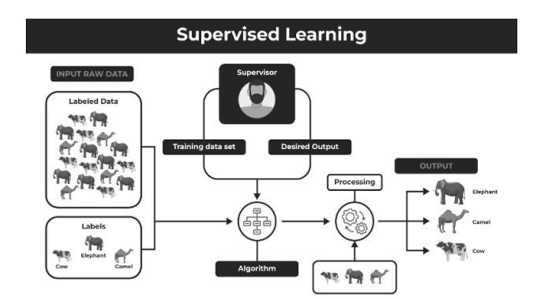
There are two main categories of supervised learning that are mentioned below:
下面提到了监督学习的两个主要类别:
- Classification 分类
- Regression 回归
Classification
分类
Classification is a type of supervised learning that focuses on predicting categorical target variables, which represent discrete classes or labels.
分类是一种监督学习,侧重于预测分类目标变量,这些变量代表离散的类别或标签。
Example 示例
Classify emails as “Spam” or “Not Spam” (Ham).
将电子邮件分类为 “垃圾邮件” 或 “非垃圾邮件” (Ham)。
Email Content 邮件内容
| Email Content | Links | Keywords | Label |
|---|---|---|---|
| “Congratulations! …” | 5 | 3 | Spam |
| “Meeting at 3 PM…” | 0 | 0 | Not Spam |
| “Special offer for you” | 2 | 2 | Spam |
Common classification algorithms include: 常见的分类算法包括:
- Logistic Regression 逻辑回归
- Decision Trees 决策树
- Random Forest 随机森林
- K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) K-近邻算法 (KNN)
- Support Vector Machines (SVMs) 支持向量机 (SVMs)
Regression
回归
Regression is a type of supervised learning that focuses on predicting continuous target variables, which represent numerical values. Unlike classification, which predicts discrete labels, regression algorithms learn to map input features to continuous numerical values.
回归是一种监督学习,侧重于预测连续的目标变量,这些变量代表数值。与预测离散标签的分类不同,回归算法学习将输入特征映射到连续的数值。
| Size | Bedrooms | Bathrooms | Location | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2 | 3 | 1 | $300,000 |
| 1500 | 1 | 2 | 3 | $200,000 |
| 1800 | 3 | 2 | 2 | $250,000 |
Common regression algorithms include: 常见的回归算法包括:
- Linear Regression 线性回归
- Decision Tree 决策树
- Polynomial Regression 多项式回归
- Random Forest 随机森林
Unsupervised Learning
无监督学习
Unsupervised learning is a machine learning technique where algorithms analyze unlabeled data to uncover patterns, relationships, and structures within the dataset. Unlike supervised learning, which relies on labeled target outputs for training, unsupervised learning does not use predefined labels. Instead, it seeks to identify hidden patterns and intrinsic structures in the data.
无监督学习是一种机器学习技术,算法分析未标记的数据以揭示数据集中的模式、关系和结构。与依赖标记目标输出进行训练的监督学习不同,无监督学习不使用预定义的标签。相反,它寻求识别数据中隐藏的模式和内在结构。
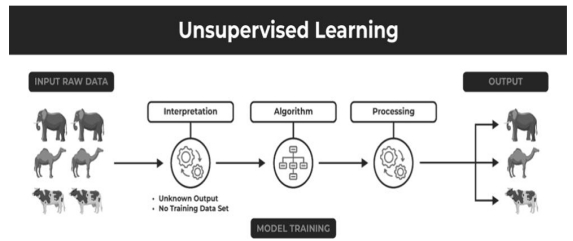
There are two main categories of unsupervised learning that are mentioned below:
下面提到了无监督学习的两个主要类别:
- Clustering 聚类
- Association 关联
Clustering
聚类
Clustering is a technique in unsupervised machine learning where data points are grouped into clusters based on their similarity or shared characteristics. It aims to organize data into meaningful structures without requiring predefined labels.
聚类是无监督机器学习中的一种技术,根据数据点的相似性或共同特征将其分组为簇。它旨在将数据组织成有意义的结构,而无需预定义的标签。
Common Clustering algorithms include: 常见的聚类算法包括:
- K-Means K-均值
- Hierarchical Clustering 层次聚类
Association
关联
Association refers to a type of unsupervised learning technique primarily used to find relationships or patterns in large datasets. In association, the goal is to identify frequent itemsets and association rules that describe how items or attributes tend to co-occur or are related to one another within the data.
关联是指一种无监督学习技术,主要用于发现大型数据集中的关系或模式。在关联中,目标是识别频繁项集和关联规则,这些规则描述了项目或属性如何在数据中倾向于共同出现或相互关联。
Common Association algorithms include: 常见的关联算法包括:
- Apriori Algorithm Apriori 算法
- FP-growth FP-growth 算法
Example 示例
Consider the following transactions at a retail store:
考虑零售店的以下交易:
| Transaction ID | Items |
|---|---|
| 1 | Milk, Bread |
| 2 | Milk, Diaper, Beer |
| 3 | Milk, Bread, Diaper |
| 4 | Milk, Bread, Beer |
| 5 | Milk, Diaper, Beer |
Frequent Itemsets: {Milk}, {Bread}, {Diaper}, {Beer}, {Milk, Bread}, {Milk, Diaper , etc.
频繁项集: {牛奶}, {面包}, {尿布}, {啤酒}, {牛奶, 面包}, {牛奶, 尿布}, 等等。
Association Rule: 关联规则: Milk → Bread: If a customer buys Milk, they are likely to buy Bread.
牛奶 → 面包: 如果顾客买了牛奶,他们很可能会买面包。
Spark MLlib
Spark MLlib
MLlib is Apache Spark’s scalable machine learning library. It provides a set of algorithms and utilities for machine learning (ML) tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, collaborative filtering, and dimensionality reduction, along with tools for evaluating and tuning models. MLlib is designed to scale efficiently across large datasets, leveraging the distributed nature of Apache Spark.
MLlib 是 Apache Spark 的可扩展机器学习库。它提供了一套用于机器学习 (ML) 任务的算法和实用程序,例如分类、回归、聚类、协同过滤和降维,以及用于评估和调整模型的工具。MLlib 旨在利用 Apache Spark 的分布式特性,在大型数据集上高效扩展。
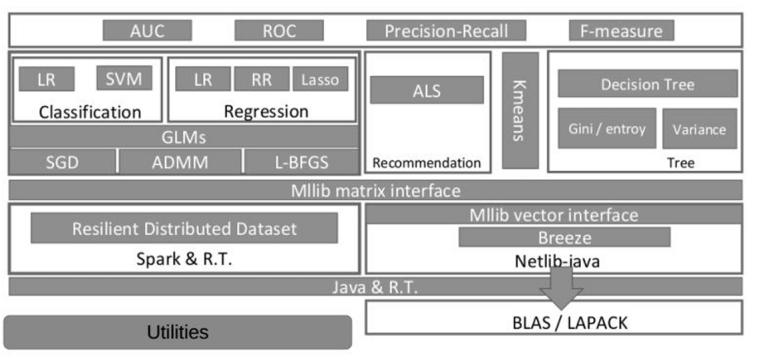
Spark MLlib Architecture
Spark MLlib 架构
Data Types
数据类型
DataFrames: Primary data structure for MLlib. Schema-based data structure containing rows and columns.
数据框 (DataFrames): MLlib 的主要数据结构。包含行和列的基于模式的数据结构。
Vectors: Supports transformations and actions for feature engineering.
向量 (Vectors): 支持特征工程的转换和操作。
1 | 0,0,5,0,3 |
Represents features or labels in machine learning models.
表示机器学习模型中的特征或标签。
Types: 类型:
DenseVector: Stores all elements explicitly.
密集向量 (DenseVector): 显式存储所有元素。
[0.0, 0.0, 5.0,0.0,3.0]SparseVector: Efficiently stores vectors with many zeros.
稀疏向量 (SparseVector): 高效存储包含许多零的向量。
(size, [indexes_of_non_zero], [values_of_non_zero])(大小, [非零索引], [非零值])(5,[2,4], [5.0,3.0])
Top Layer: Evaluation Metrics
顶层:评估指标
Defines the evaluation metrics to assess model performance:
定义用于评估模型性能的评估指标:
AUC (Area Under Curve): Used for classification tasks, especially binary classification.
AUC (曲线下面积): 用于分类任务,特别是二分类。
ROC (Receiver Operating Characteristic): A curve to evaluate the model’s ability to distinguish between classes.
ROC (受试者工作特征): 用于评估模型区分类别能力的曲线。
Precision-Recall: Used to evaluate performance in imbalanced classification tasks.
精确率-召回率: 用于评估不平衡分类任务中的性能。
F-measure: Balances precision and recall.
F-度量: 平衡精确率和召回率。
2. Second Layer: Core MLlib Algorithms
2. 第二层:核心 MLlib 算法
Describes key machine learning algorithms in Spark MLlib:
描述 Spark MLlib 中的关键机器学习算法:
Classification: Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machines.
分类: 逻辑回归,支持向量机。
Regression: Linear Regression, Ridge Regression, Lasso.
回归: 线性回归,岭回归,Lasso。
Clustering: K-means, Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM).
聚类: K-均值,高斯混合模型 (GMM)。
Recommendation: Alternating Least Squares (ALS).
推荐: 交替最小二乘法 (ALS)。
3. Third Layer: Optimization Techniques
3. 第三层:优化技术
Focuses on the optimization methods used to train models:
侧重于用于训练模型的优化方法:
SGD (Stochastic Gradient Descent): Updates parameters incrementally.
SGD (随机梯度下降): 增量更新参数。
ADMM: Optimizes constrained problems.
ADMM: 优化约束问题。
L-BFGS: Limited-memory optimization technique.
L-BFGS: 有限内存优化技术。
GLMS (Generalized Linear Models): A framework that generalizes regression models.
GLMS (广义线性模型): 推广回归模型的框架。
4. Fourth Layer: Core Computational Components
4. 第四层:核心计算组件
Key components for distributed computation:
分布式计算的关键组件:
RDD (Resilient Distributed Dataset): Distributed data structure for parallel processing.
RDD (弹性分布式数据集): 用于并行处理的分布式数据结构。
MLlib Matrix Interface: Interface for matrix operations.
MLlib 矩阵接口: 矩阵运算的接口。
MLlib Vector Interface: Efficient handling of feature vectors.
MLlib 向量接口: 特征向量的高效处理。
5. Fifth Layer: Spark & Libraries
5. 第五层:Spark 与库
Integration with Spark and libraries:
与 Spark 和库的集成:
Spark & Runtime: Distributed computing for scalability.
Spark 与运行时: 用于可扩展性的分布式计算。
Breeze: Numerical processing library.
Breeze: 数值处理库。
Netlib-java: Optimized linear algebra routines.
Netlib-java: 优化的线性代数例程。
BLAS/LAPACK: Libraries for linear algebra operations.
BLAS/LAPACK: 线性代数运算库。
6. Bottom Layer: Utilities
6. 底层:实用工具
Provides utilities for:
提供以下实用工具:
Model evaluation: Use metrics to assess models.
模型评估: 使用指标评估模型。
Hyperparameter tuning: Optimizing hyperparameters.
超参数调整: 优化超参数。
Model saving/loading: Persisting models for future predictions.
模型保存/加载: 持久化模型以供将来预测。
Workflow in MLlib
MLlib 中的工作流程
1. Data Preparation: Load data into DataFrames. Preprocess data (e.g., missing value handling, encoding categorical variables).
- 数据准备: 将数据加载到 DataFrame 中。预处理数据(例如,缺失值处理,编码分类变量)。
2. Pipeline Construction: Build a pipeline of Transformers and Estimators.
- 管道构建: 构建转换器 (Transformers) 和评估器 (Estimators) 的管道。
3. Model Training: Train the model on training data using distributed algorithms.
- 模型训练: 使用分布式算法在训练数据上训练模型。
4. Model Evaluation: Use evaluation metrics to test model performance.
- **模型评估:**使用评估指标测试模型性能。
5. Model Deployment: Save the model and use it for predictions on new data.
- **模型部署:**保存模型并将其用于新数据的预测。
Advantages of Spark MLlib
Spark MLlib 的优势
Scalability: Designed for large-scale data.
可扩展性: 专为大规模数据设计。
Flexibility: Supports multiple languages.
灵活性: 支持多种语言。
Integration: Works seamlessly with Spark’s ecosystem.
集成: 与 Spark 生态系统无缝协作。
Ease of Use: Provides a high-level API for machine learning pipelines.
易用性: 为机器学习管道提供高级 API。
This architecture ensures that MLlib is not only efficient for distributed processing but also user-friendly for developers and data scientists.
这种架构确保 MLlib 不仅在分布式处理方面高效,而且对开发人员和数据科学家也很友好。