Chapter 7
第7章
Spark Streaming is an extension of Apache Spark that enables scalable, high-throughput, fault-tolerant stream processing of real-time data streams.
Spark Streaming 是 Apache Spark 的一个扩展,它支持对实时数据流进行可扩展、高吞吐量、容错的流处理。
It allows you to process real-time data from various sources such as Kafka, Flume, Kinesis, or TCP sockets, and perform complex computations on this data using the Spark API.
它允许你处理来自各种来源(如 Kafka、Flume、Kinesis 或 TCP 套接字)的实时数据,并使用 Spark API 对这些数据执行复杂的计算。

Features of Spark Streaming
Spark Streaming 的特性
1. Ease of Use:
1. 易用性:
Integrates seamlessly with the Spark API, allowing users to apply the same operations to streaming data as to batch data.
与 Spark API 无缝集成,允许用户像处理批处理数据一样对流数据应用相同的操作。
2. Fault Tolerance:
2. 容错性:
Provides end-to-end fault tolerance guarantees through Spark’s native resilient distributed datasets (RDDs).
通过 Spark 原生的弹性分布式数据集 (RDD) 提供端到端的容错保证。
3. Scalability:
3. 可扩展性:
Leverages Spark’s distributed processing power, enabling it to scale efficiently with large data volumes.
利用 Spark 的分布式处理能力,使其能够随着大数据量高效扩展。
4. Integration with Batch and Interactive Queries:
4. 与批处理和交互式查询的集成:
Allows usage of Spark SQL queries for both batch and streaming data, simplifying the development and maintenance of code.
允许对批处理和流数据同时使用 Spark SQL 查询,简化了代码的开发和维护。
5. Advanced Analytics:
5. 高级分析:
Supports advanced analytics like windowed computations, joins, and aggregations over streams.
支持流上的高级分析,如窗口计算、连接 (joins) 和聚合。
Core Concepts
核心概念
Discretized Stream (DStream):
离散化流 (DStream):
The main abstraction in Spark Streaming. It represents a continuous stream of data as a series of RDDs, which are immutable distributed collections of objects.
Spark Streaming 中的主要抽象。它将连续的数据流表示为一系列 RDD,即不可变的分布式对象集合。
Input DStreams:
输入 DStream:
These are streams of data received from a source, such as Kafka or Flume.
这些是从源(如 Kafka 或 Flume)接收的数据流。
Transformations:
转换 (Transformations):
Operations on DStreams that yield other DStreams, like map, filter, reduce, etc.
对 DStream 的操作,用于生成其他 DStream,例如 map、filter、reduce 等。
Output Operations:
输出操作:
Operations that write data to an external system, like saveAsTextFiles, saveAsObjectFiles, saveAsHadoopFiles, foreachRDD, etc.
将数据写入外部系统的操作,例如 saveAsTextFiles、saveAsObjectFiles、saveAsHadoopFiles、foreachRDD 等。
Spark Streaming System Structure
Spark Streaming 系统结构
A DStream represents a continuous stream of data divided into small, manageable batches. Built on RDDS (Resilient Distributed Datasets), which are Spark’s core data abstraction, DStreams enable seamless integration with other Spark components, such as MLlib and Spark SQL.
DStream 表示被划分为小的、可管理的批次的连续数据流。DStream 建立在 Spark 的核心数据抽象 RDD(弹性分布式数据集)之上,能够与其他 Spark 组件(如 MLlib 和 Spark SQL)无缝集成。
Unlike other systems that either have dedicated processing engines for streaming or separate batch and streaming APIs compiled to different engines, Spark Streaming uses a single execution engine and a unified programming model for both batch and streaming data.
与其他拥有专用流处理引擎或将批处理和流 API 编译到不同引擎的系统不同,Spark Streaming 对批处理和流数据使用单一的执行引擎和统一的编程模型。
This approach offers significant advantages over traditional streaming systems, particularly in terms of simplicity and efficiency.
这种方法相比传统流处理系统具有显著优势,特别是在简单性和效率方面。
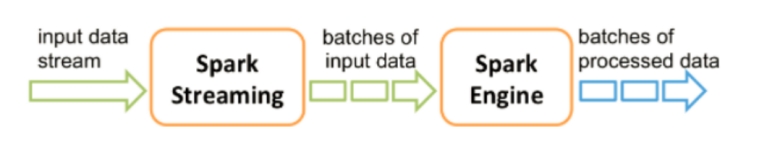
DStream
DStream (离散化流)
A DStream (Discretized Stream) is the core abstraction in Spark Streaming. It represents a continuous stream of data as a series of Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs), enabling Spark Streaming to process both real-time streaming and batch data with a unified approach.
DStream(离散化流)是 Spark Streaming 的核心抽象。它将连续的数据流表示为一系列弹性分布式数据集 (RDD),使 Spark Streaming 能够以统一的方式处理实时流数据和批处理数据。
A DStream is essentially a sequence of RDDs, where each RDD corresponds to data received over a specific time interval. This discrete nature allows Spark Streaming to leverage the power of the RDD API for efficient stream processing.
DStream 本质上是一个 RDD 序列,其中每个 RDD 对应于特定时间间隔内接收的数据。这种离散特性允许 Spark Streaming 利用 RDD API 的强大功能进行高效的流处理。
DStreams can be created from various input sources such as Kafka, Flume, Kinesis, and TCP sockets. You can apply common RDD transformations to DStreams, like map, flatMap, filter, reduceByKey, and window, enabling you to build complex data processing pipelines.
DStream 可以从各种输入源(如 Kafka、Flume、Kinesis 和 TCP 套接字)创建。你可以对 DStream 应用常见的 RDD 转换,如 map、flatMap、filter、reduceByKey 和 window,从而构建复杂的数据处理管道。
Finally, output operations allow you to write processed data to external systems, such as HDFS, databases, or live dashboard.
最后,输出操作允许你将处理后的数据写入外部系统,如 HDFS、数据库或实时仪表板。
How DStream Works
DStream 如何工作
To understand how DStreams work, it’s important to grasp the fundamental mechanics of how Spark Streaming processes data in a fault-tolerant and scalable manner. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how DStreams operate:
要理解 DStream 如何工作,重要的是掌握 Spark Streaming 如何以容错和可扩展的方式处理数据的基本机制。以下是 DStream 操作的分步说明:
1. Data Ingestion
1. 数据摄入
Spark Streaming receives data from various sources such as Kafka, Flume, TCP sockets, or any custom data source. Spark Streaming 从各种来源(如 Kafka、Flume、TCP 套接字或任何自定义数据源)接收数据。
Data is ingested in small time intervals (e.g., every 1 second) and is stored in Spark’s memory.
数据以小的时间间隔(例如每 1 秒)被摄入并存储在 Spark 的内存中。
2. Batch Creation - Micro-Batch Processing
2. 批次创建 - 微批处理
Incoming data is divided into small batches represented by RDDs, which are processed in intervals.
传入的数据被划分为由 RDD 表示的小批次,并在间隔内进行处理。
3. Transformations
3. 转换
Applying Transformations:
应用转换:
Transformations on DStreams are operations that produce a new DStream.
DStream 上的转换是产生新 DStream 的操作。
These transformations are applied to each RDD within the DStream.
这些转换应用于 DStream 中的每个 RDD。
Common Transformations: 常见转换:
- map: Applies a function to each element.
- map: 对每个元素应用一个函数。
- flatMap: Similar to map, but each input item can map to 0 or more output items.
- flatMap: 类似于 map,但每个输入项可以映射到 0 个或多个输出项。
- filter: Filters elements based on a predicate.
- filter: 根据谓词过滤元素。
- reduceByKey: Combines values with the same key.
- reduceByKey: 合并具有相同键的值。
- window: Aggregates elements over a sliding window.
- window: 在滑动窗口上聚合元素。
4. RDD Generation
4. RDD 生成
Generating RDDs:
生成 RDD:
A new RDD is created for each time interval, containing the data received during that interval.
每个时间间隔都会创建一个新的 RDD,包含该间隔期间接收的数据。
Transformations on DStreams result in a corresponding transformation on the underlying RDDs.
DStream 上的转换会导致底层 RDD 上的相应转换。
5. Fault Tolerance
5. 容错性
Fault Tolerance Mechanism: 容错机制:
DStreams use lineage graphs and RDDs to ensure data can be recomputed if lost.
DStream 使用血统图 (lineage graphs) 和 RDD 来确保数据丢失时可以重新计算。
If data is lost, it can be recomputed using the original transformations.
如果数据丢失,可以使用原始转换重新计算。
6. Output Operations
6. 输出操作
Writing Data: 写入数据:
Output operations push the processed data to external systems such as HDFS, databases, or live dashboards.
输出操作将处理后的数据推送到外部系统,如 HDFS、数据库或实时仪表板。
Some common output operations include pprint, saveAsTextFiles, saveAsHadoopFiles, and foreachRDD.
一些常见的输出操作包括 pprint、saveAsTextFiles、saveAsHadoopFiles 和 foreachRDD。
7. Execution
7. 执行
Starting the Streaming Context:
启动流上下文:
The StreamingContext needs to be started to begin processing the data.
需要启动 StreamingContext 才能开始处理数据。
The processing continues until the streaming context is stopped manually or due to an error.
处理将持续进行,直到手动停止流上下文或发生错误。
Window Operation
窗口操作
Window operations in Spark Streaming allow the processing of data over specified time windows rather than just individual chunks of data.
Spark Streaming 中的窗口操作允许在指定的时间窗口上处理数据,而不仅仅是单个数据块。
Sometimes you want to look at the data over a longer period of time instead of just individual chunks. This is where window operations come in.
有时你需要查看较长时间段内的数据,而不仅仅是单个块。这就是窗口操作发挥作用的地方。
A window operation lets you look at a stream of data over a specified period (window duration) and update the results at regular intervals (sliding interval).
窗口操作允许你在指定的时间段(窗口长度)内查看数据流,并定期更新结果(滑动间隔)。
Key Terms
关键术语
- Window Duration: How long the time window is (e.g., 30 sec).
- 窗口长度: 时间窗口有多长(例如 30 秒)。
- Sliding Interval: How often the window slides forward to process the next set of data (e.g., 10 sec).
- 滑动间隔: 窗口向前滑动以处理下一组数据的频率(例如 10 秒)。
Example
示例
For a stream of data (e.g., chat messages), you can count messages over the last 2 minutes, updated every 1 minutes.
对于数据流(例如聊天消息),你可以统计过去 2 分钟内的消息,每 1 分钟更新一次。
Imagine you have a stream of data coming in every second, like chat messages from a chatroom. You want to count the number of messages over the last 2 minutes, but you want to update this count every 1 minute.
想象一下,你每秒都有数据流进来,比如来自聊天室的聊天消息。你想统计过去 2 分钟内的消息数量,但你想每 1 分钟更新一次这个计数。
This way, you can see how many messages were sent in the last 2 minutes, updated every 1 minute.
这样,你可以看到过去 2 分钟内发送了多少条消息,且每 1 分钟更新一次。
Window Duration (2 Minutes): This is the length of time we are looking at to count the messages. Every count will include messages from the last 2 minutes.
窗口长度(2 分钟): 这是我们用来统计消息的时间长度。每次统计将包含过去 2 分钟内的消息。
Sliding Interval (1 Minutes): This is how often we update our count. Every 1 minutes, Spark will print the count of messages from the last 2 minutes.
滑动间隔(1 分钟): 这是我们更新计数的频率。每 1 分钟,Spark 将打印过去 2 分钟的消息计数。
We can say, every minute I want to know, how many messages we have received in last 2 minutes.
我们可以说,每分钟我都想知道,我们在过去 2 分钟内收到了多少条消息。
Count 2 Minutes Messages
统计 2 分钟内的消息
| Window time (2M) 窗口时间 (2分钟) | Sliding interval (update time) 滑动间隔 (更新时间) | Message 消息 |
|---|---|---|
| 18:59 to 9:01 | 9:01 | total message are 10 million (消息总数 1000 万) |
| 9:00 to 9:02 | 9:02 | total message are 5 million (消息总数 500 万) |
| 19:01 to 9:03 | 9:03 | total messages are 4 million (消息总数 400 万) |
| 19:02 to 9:04 | 9:04 | total message are 7 million (消息总数 700 万) |
| 9:04 to 9:05 | 9:05 | total message are 6 million (消息总数 600 万) |
Windows Function
窗口函数
window:
window:
Calculate a new DStream based on the windowed batch data generated by the source DStream.
基于源 DStream 生成的窗口批处理数据计算新的 DStream。
- Usage: Groups the data in a DStream into larger time windows.
- 用法: 将 DStream 中的数据分组到更大的时间窗口中。
- Example: Grouping lines of data into 30-second windows and updating every 10 seconds.
- 示例: 将数据行分组为 30 秒的窗口,并每 10 秒更新一次。
countByWindow:
countByWindow:
- Usage: Counts the number of elements in a DStream over a sliding window.
- 用法: 统计滑动窗口内 DStream 中的元素数量。
- Example: Counting the number of lines in a 30-second window sliding every 10 seconds.
- 示例: 统计 30 秒窗口内的行数,每 10 秒滑动一次。
reduceByWindow:
reduceByWindow:
- Usage: Reduces elements in a DStream over a sliding window using a specified function.
- 用法: 使用指定函数在滑动窗口上规约 (reduce) DStream 中的元素。
- Example: Summing numbers in a 30-second window sliding every 10 seconds.
- 示例: 对 30 秒窗口内的数字求和,每 10 秒滑动一次。
reduceByKeyAndWindow:
reduceByKeyAndWindow:
- Usage: Reduces key-value pairs over a sliding window using a specified function.
- 用法: 使用指定函数在滑动窗口上规约键值对。
- Example: Counting words over a 30-second window sliding every 10 seconds.
- 示例: 统计 30 秒窗口内的单词数,每 10 秒滑动一次。
countByValueAndWindow:
countByValueAndWindow:
- Usage: Counts the occurrence of each value in a DStream over a sliding window.
- 用法: 统计滑动窗口内 DStream 中每个值的出现次数。
- Example: Counting occurrences of words in a 30-second window sliding every 10 seconds.
- 示例: 统计 30 秒窗口内单词的出现次数,每 10 秒滑动一次。
groupByKeyAndWindow:
groupByKeyAndWindow:
- Usage: Groups values of each key in a DStream over a sliding window.
- 用法: 将滑动窗口内 DStream 中每个键的值进行分组。
- Example: Grouping values by key over a 30-second window sliding every 10 seconds.
- 示例: 按键将值分组,在 30 秒窗口内,每 10 秒滑动一次。
Maven Dependency
Maven 依赖
1 | <dependency> |