Chapter 4
第 4 章
RDD (Resilient Distributed Dataset) is Spark’s core low-level abstraction. An RDD is an immutable, partitioned collection of elements that can be processed in parallel. It is resilient because Spark can recompute lost partitions using the RDD’s lineage (the sequence of operations that created it).
RDD(弹性分布式数据集)是 Spark 的核心底层抽象。RDD 是一种不可变、分区化的元素集合,可被并行处理。之所以称为弹性,是因为 Spark 能根据 RDD 的血统信息(生成它的一系列操作)重新计算丢失的分区。
In Spark, all the data operations are nothing more than creating RDD, transforming RDD and calling RDD operations for evaluation. Behind the scenes, Spark automatically distributes data from RDD to clusters and parallelizes operations.
在 Spark 中,所有数据操作本质上就是创建 RDD、对 RDD 做转换,并在求值时调用 RDD 的动作操作。底层由 Spark 自动将 RDD 的数据分发到集群各处并并行化执行。
Partitioned: data is split into partitions that executors process in parallel.
分区化:数据被切分为多个分区,由各个 Executor 并行处理。
Each partition processed by Task.
每个分区由一个或多个**任务(Task)**处理。
Creating RDD
创建 RDD
RDD is created in two ways
RDD 的创建有两种方式
- Parallelize a local collection.
- 并行化本地集合。
- Read external data sets and create them from input from the Hadoop file system (or other Hadoop compatible persistent storage systems, such as Hive, Cassandra, HBase) (such as HDFS).
- 从外部数据集读取并创建,例如 Hadoop 文件系统(或其他兼容 Hadoop 的持久化存储系统,如 Hive、Cassandra、HBase),如 HDFS。
1 | val data = Seq(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) |
Generate RDD from external source(HDFS, Local)
从外部源(HDFS、本地)生成 RDD
1 | val lines = sc.textFile("/path/README.md") |
Spark RDD Operator
Spark RDD 操作
- Input: During Spark, data is read from external data space (such as distributed storage: textFile)HDFS, etc., and parallelize methods to enter Scala collections or data) into Spark, which goes into the Spark runtime data null and convert into data blocks in Spark for management through BlockManager.
- 输入:在 Spark 中,数据可从外部数据空间读取(如分布式存储:textFile 读 HDFS 等),或通过 parallelize 将 Scala 集合数据送入 Spark。数据进入 Spark 运行时后被切分为数据块,由 BlockManager 统一管理。
- Operation: After Spark data input forms RDD, data can be operated by transformation operator, such as Filter, etc. Make and convert RDD into the new RDD, and trigger Spark to submit the job through the Action operator. If the data needs to be reused, you can use the Cache operator to Cache the data into memory
- 操作:形成 RDD 后可通过**转换(Transformation)算子(如 filter 等)生成新的 RDD,并通过动作(Action)**算子触发作业提交。若数据需要复用,可使用缓存(cache/persist)将其存入内存。
- Output: The program run end data will output Spark runtime space and be stored in distributed storage (e.g SaveAsTextFile output to HDFS, or Scala data or collection (Collect output to Scala collection, count returns Scala int data.
- 输出:程序结束时数据可从 Spark 运行时输出,存入分布式存储(如 saveAsTextFile 输出到 HDFS),或返回到 Driver(如 collect 返回 Scala 集合,count 返回整型数量)。
Difference Between SparkContext and SparkSession
SparkContext 与 SparkSession 的区别
| Feature / 特性 | **SparkContext ** | SparkSession |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | Spark 1.x (older API) | Spark 2.0 (newer unified API) |
| 介绍 | Spark 1.x(较旧的 API) | Spark 2.0(更新的统一 API) |
| Main Purpose | Entry point for working with RDDs (low-level API) | Entry point for DataFrames, Datasets, and SQL |
| 主要用途 | 处理 RDD 的入口(底层 API) | DataFrame、Dataset 与 SQL 的入口 |
| Level of Abstraction | Lower-level (RDD-based operations) | Higher-level (DataFrame, Dataset, SQL-based operations) |
| 抽象层级 | 较低(基于 RDD 的操作) | 较高(基于 DataFrame、Dataset、SQL 的操作) |
| Data Sources Supported | Limited to basic file formats (text, Hadoop) | Supports a wide variety of data sources (CSV,JSON, Parquet, ORC, Hive, etc.) |
| 支持的数据源 | 仅限基础文件格式(文本、Hadoop) | 支持多种数据源(CSV、JSON、Parquet、ORC、Hive 等) |
| Ease of Use | More complex, requires manual RDD management | Simplifies data handling with DataFrames/Datasets |
| 易用性 | 更复杂,需要手动管理 RDD | 通过 DataFrame/Dataset 简化数据处理 |
| SQL Support | Not directly supported | Built-in SQL support (can run SQL queries) |
| SQL 支持 | 不直接支持 | 内置 SQL 支持(可运行 SQL 查询) |
| Hive Support | Requires HiveContext | Built-in Hive support |
| Hive 支持 | 需要 HiveContext | 内置 Hive 支持 |
| DataFrame API | Not available | Primary focus on DataFrames/Datasets |
| DataFrame API | 不可用 | 以 DataFrame/Dataset 为核心 |
| Creation | val sc = new SparkContext(conf) | val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName(“App”).getOrCreate() |
| 创建方式 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf) | val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName(“App”).getOrCreate() |
| RDD Access | Yes | Yes, via spark.sparkContext |
| 访问 RDD | 可以 | 可以,通过 spark.sparkContext |
| Deprecation | Still available but considered legacy | Preferred and modern way to interact with Spark |
| 弃用状态 | 仍可用但被视为遗留方式 | 目前更推荐、更现代的交互方式 |
RDD’s Operation
RDD 的操作
RDD supports two types of operations: transformations (creating new sets of data from existing ones) and actions (operations that return values to the driver after they have been evaluated). For example, a map is a transformation that passes each data set element through a function and returns a new RDD representing the result. Reduce, on the other hand, is an operation that USES a function to aggregate all elements of RDD and return the final result to the driver (although there is also a parallel reduce By Key to return the distributed dataset).
RDD 支持两类操作:转换(transformation)(从已有数据生成新数据集)与动作(action)(触发计算并把结果返回给 Driver 或写出)。例如 map 是把每个元素经函数处理后返回一个新 RDD 的转换;而 reduce 则用给定函数聚合 RDD 的所有元素并把最终结果返回给 Driver(也有按键聚合的 reduceByKey 等分布式形式)。
Transformation
转换(Transformation)
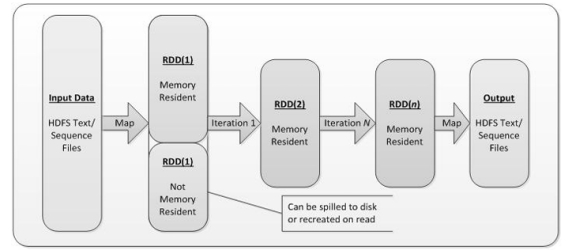
Transformations are operations that create a new RDD/DataFrame from an existing one. These are lazy operations, meaning that they don’t immediately execute when called but instead build up a transformation plan (also called a Directed Acyclic Graph, or DAG). The actual execution happens only when an Action is invoked.
转换操作会基于已有 RDD/DataFrame 创建新的 RDD/DataFrame。它们是惰性的:调用时不会立即执行,而是构建一条转换计划(有向无环图,DAG)。只有在调用动作时才真正执行。
Transformations define a data pipeline and are lazy, meaning they are not executed until an Action is called.
转换定义了数据流水线,并以惰性方式延迟到动作触发时执行。
Transformations are immutable. They do not modify the existing RDD or DataFrame but create a new one.
转换是不可变的:不会修改原有 RDD 或 DataFrame,而是创建新的。
Why is Lazy Evaluation Important
为什么惰性求值很重要Lazy evaluation allows Spark to optimize the sequence of operations and reduce the number of passes over the data. This optimization helps reduce the overall execution time and resource usage.
惰性求值使 Spark 能优化操作序列并减少对数据的扫描次数,从而降低总体执行时间与资源消耗。
| Transformation Operation / 转换操作 | Description / 描述 |
|---|---|
| map(func) | Call func on each element in the source RDD to generate new elements, these new elements form a new RDD and return |
| map(func) | 对每个元素调用函数,生成新元素并组成新 RDD 返回 |
| flatMap(func) | Similar to map, but each input RDD member can produce 0 or more input members(so the return value of func is of type Seq) |
| flatMap(func) | 类似 map,但每个输入可产生 0 个或多个输出,函数返回 Seq |
| filter(func) | Filter the RDD, call func on each element in the original RDD, and if it returns true, keep the element, form a new RDD from these elements and return |
| filter(func) | 按条件保留元素,返回仅包含满足条件元素的新 RDD |
| mapPartitions(func) | Similar to map, but func acts on an entire partition: Iterator<T> => Iterator<U> |
| mapPartitions(func) | 按分区处理:Iterator<T> => Iterator<U> |
| mapPartitionsWithIndex(func) | Like mapPartitions but also provides partition index: (Int, Iterator<T>) => Iterator<U> |
| mapPartitionsWithIndex(func) | 提供分区索引的按分区处理 |
| sample(withReplacement, fraction, seed) | Sample the RDD with/without replacement; fraction is sampling ratio; seed is RNG seed |
| sample(withReplacement, fraction, seed) | 是否放回、采样比例、随机种子 |
| union(otherDataset) | Merge two RDDs without de-duplication; element types must match |
| union(otherDataset) | 合并两个 RDD,不去重;元素类型需一致 |
| distinct(numTasks) | Remove duplicates from the original RDD and return a de-duplicated RDD |
| distinct(numTasks) | 对 RDD 去重,返回无重复元素的 RDD |
| groupByKey(numTasks) | Group values by key into (key, Iterable[value]) (involves shuffle; prefer reduceByKey/aggregateByKey for aggregation) |
| groupByKey(numTasks) | 按键分组为 (key, Iterable[value]);涉及 shuffle;聚合更推荐 reduceByKey/aggregateByKey |
| reduceByKey(func, [numTasks]) | Aggregate values with same key using (V, V) => V (does map-side combine then shuffle) |
| reduceByKey(func, [numTasks]) | 用 (V,V)=>V 按键聚合,先本地合并再 shuffle,更高效 |
| sortByKey([ascending], [numTasks]) | Sort a (key, value) RDD ascending/descending |
| sortByKey([ascending], [numTasks]) | 对键值 RDD 升/降序排序 |
| join(otherDataset, [numTasks]) | Join (k,v) with (k,w) to get (k,(v,w)); also leftOuterJoin/rightOuterJoin/fullOuterJoin |
| join(otherDataset, [numTasks]) | 按键连接,支持内连接及左/右/全外连接 |
Types of Transformations
转换的类型
1. Narrow Transformations
1. 窄依赖转换
Narrow transformations are those in which each partition of the parent RDD/DataFrame is used by at most one partition of the child RDD/DataFrame. There’s no need to shuffle data between partitions, meaning the data does not move across the cluster, making these transformations faster and more efficient.
窄依赖转换指父 RDD/DataFrame 的每个分区最多只被一个子分区使用,无需在分区之间打散重分配(无 shuffle),因此数据不跨节点移动,执行更快更高效。
Ex :- Map, filter, flatmap, mappartitions
例如:map、filter、flatMap、mapPartitions
2. Wide Transformations
2. 宽依赖转换
Wide transformations are those where data from multiple partitions of the parent RDD/DataFrame is needed by one or more partitions of the child RDD/DataFrame. This requires a shuffle operation, where data is redistributed across the cluster. Shuffling involves disk I/O, network I/O, and sorting, making these transformations more expensive in terms of time and resources.
宽依赖转换指子分区需要来自父 RDD/DataFrame 多个分区的数据,需进行shuffle(跨集群重分配),涉及磁盘 I/O、网络 I/O 和排序,代价更高。
Ex:- GroupByKey, ReduceByKey, join
例如:groupByKey、reduceByKey、join
Functions
常用函数
Map Function
Map 函数
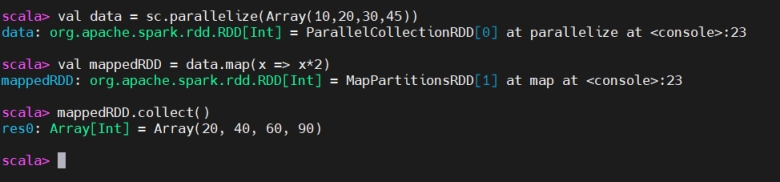
The map() transformation applies a function to each element in the RDD (or DataFrame) and returns a new RDD with the results. It is a one-to-one transformation, meaning for each input element, there is exactly one output element.
map() 对 RDD(或 DataFrame)的每个元素应用函数并返回结果组成的新 RDD。它是一对一转换:每个输入对应恰好一个输出。
The output is not flattened; it retains the structure of the input RDD or DataFrame
输出不会被扁平化;保留输入的结构层级。
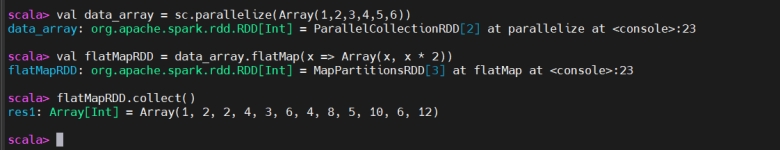
FlatMap
FlatMap
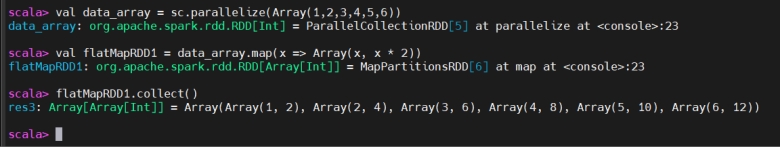
The flatMap() transformation is similar to map(), but it allows returning multiple values for each input element. It flattens the results, meaning the output is a single-level collection.
flatMap() 与 map() 类似,但允许每个输入元素返回多个值,并会对结果进行扁平化,输出为单层集合。
The output is flattened into a single collection
输出被扁平化为一个集合。
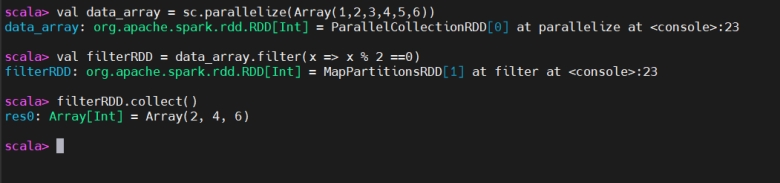
Filter
Filter 过滤
The filter() transformation returns a new RDD containing only the elements that satisfy a given condition. It’s used to filter elements based on some condition.
filter() 返回仅包含满足条件元素的新 RDD,用于按条件筛选数据。
You use filter() when you need to filter the data according to particular condition.
当需要依据特定条件过滤数据时使用 filter()。
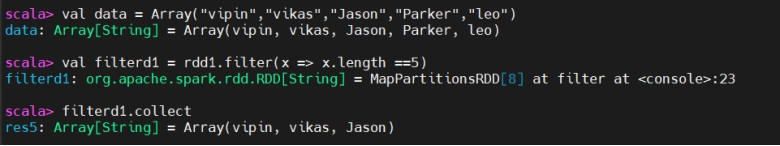
If data length is equal to 5 then return otherwise, drop it.
若数据长度等于 5 则保留,否则丢弃。
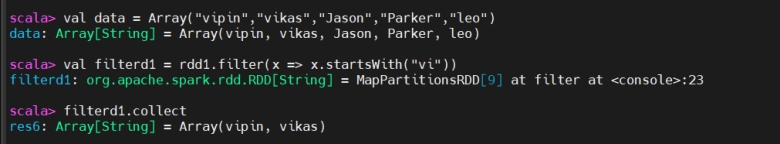
if word start with “vi” then return the result otherwise, drop it.
若单词以 “vi” 开头则保留,否则丢弃。
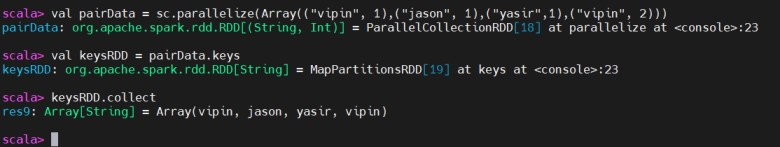
Keys
Keys(取键)
keys will only return the key in the Pair RDD to form a new RDD.
keys 仅返回二元组 RDD 中的键,形成新的 RDD。
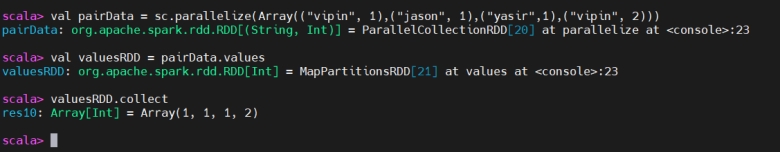
Values
Values(取值)
values will only return the values in the Pair RDD to form a new RDD.
values 仅返回二元组 RDD 中的值,形成新的 RDD。
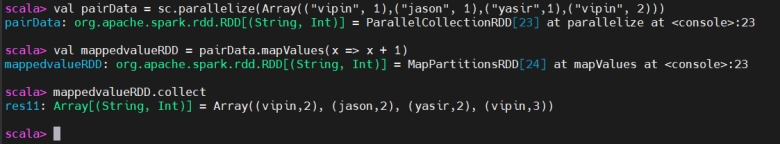
MapValues
MapValues(仅映射值)
The mapValues() function operates only on the values of the key-value pairs while preserving the keys.
mapValues() 只作用于键值对中的值,保留原有键。
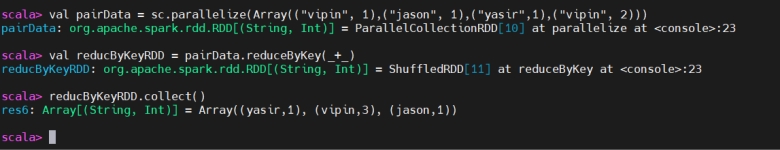
ReduceByKey
ReduceByKey(按键聚合)
The reduceByKey() transformation combines values for each key using a specified binary operation (like addition or multiplication). It performs the reduce operation locally first, then shuffles the reduced values across the cluster to get the final result. It’s more efficient than groupByKey() for aggregation.
reduceByKey() 使用给定的二元运算(如加法、乘法)合并相同键的值。它先在本地预聚合,再将聚合后的结果进行 shuffle,因此比 groupByKey() 做聚合更高效。
You use reduceByKey() when you want to aggregate values for each key.
当需要对每个键进行聚合时使用 reduceByKey()。
GroupByKey
GroupByKey(按键分组)
The groupByKey() transformation groups data by key, returning an RDD of (K, Iterable[V]) pairs where K is the key and Iterable[V] contains all values associated with that key. This operation involves shuffling data across the cluster to group values by key.
groupByKey() 按键对数据分组,返回 (K, Iterable[V]) 形式的 RDD。它涉及跨集群的shuffle 来按键聚合所有值。
you use groupByKey() when you want to group all the values for each key together.
当你需要把同一键的所有值聚到一起时使用 groupByKey()。
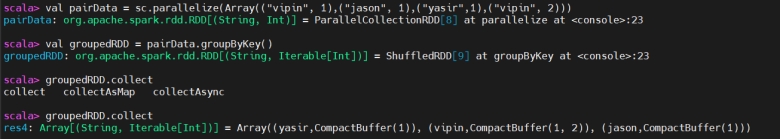
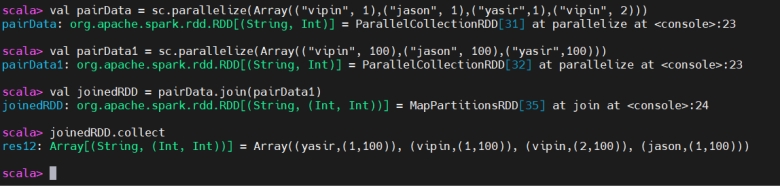
Join
Join(连接)
join() is used to combines two key-value pair RDDs based on their keys. This is similar to a SQL INNER JOIN, where only the matching keys from both datasets are included in the result.
join() 用于按键连接两个键值对 RDD,类似 SQL 的内连接,仅包含两侧都存在的键。
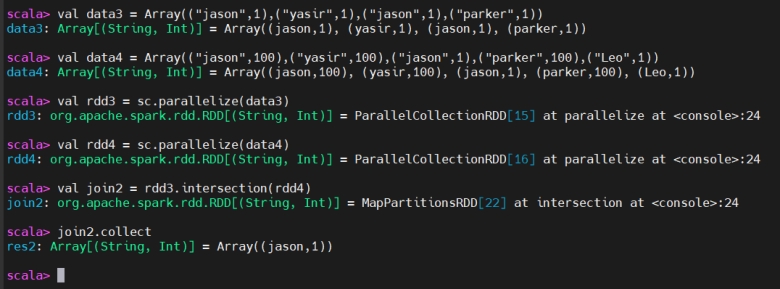
Intersection
Intersection(交集)
The intersection transformation in Apache Spark is used to find common elements between two RDDs (Resilient Distributed Datasets) or DataFrames.
Spark 的 intersection 转换用于求两个 RDD 或 DataFrame 的公共元素。
the intersection operation will match both the key and the value.
对于键值对 RDD,交集需要键和值都相同才算匹配。
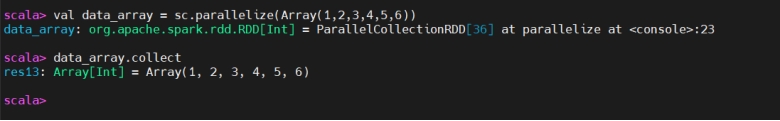
Actions
动作(Actions)
Actions trigger the execution of the transformations that have been defined. When an action is called, Spark processes the transformations and returns the result to the driver or writes it to an external storage system (e.g. HDFS).
动作会触发之前定义的所有转换执行。调用动作时,Spark 执行转换并将结果返回给 Driver,或写入外部存储(如 HDFS)。
Collect
Collect(收集到本地)
Collect is an action that retrieves the entire dataset (RDD or DataFrame) from the distributed cluster to the driver program as an array or collection.
collect 是一个动作,将整个数据集(RDD 或 DataFrame)从集群取回至 Driver 端,作为数组或集合。
you typically use collect when you want to view or process the entire dataset locally.
当需要在本地查看或处理整个数据集时通常使用 collect。
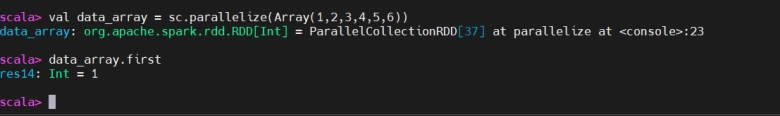
First
first(取首元素)
first() is an action that returns the first element of an RDD or DataFrame.
first() 是一个动作,返回 RDD 或 DataFrame 的第一个元素。
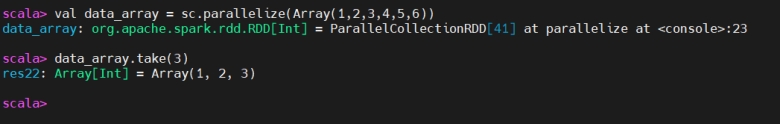
take
take(取前 N 个)
take(n) is an action that returns the first n elements from the RDD or DataFrame.
take(n) 是一个动作,返回数据集的前 n 个元素。
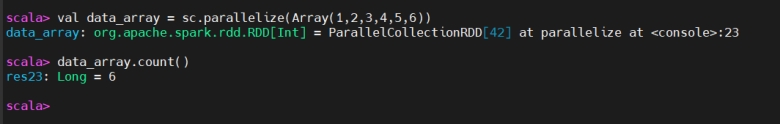
count
count(计数)
count() is an action that returns the number of elements in an RDD or DataFrame.
count() 是一个动作,返回 RDD 或 DataFrame 中元素的数量。
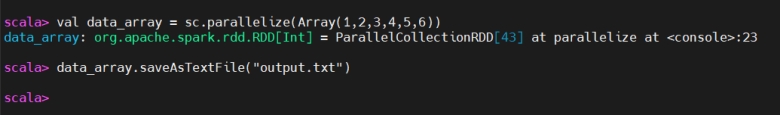
saveAsTextFile()
saveAsTextFile(保存为文本)
saveAsTextFile() is an action that writes the contents of the RDD (or DataFrame) to a directory as a series of text files. Each partition of the RDD is saved as a separate text file in the specified directory.
saveAsTextFile() 是一个动作,将 RDD(或 DataFrame)的内容写入某个目录下的一系列文本文件。每个分区各生成一个文本文件。
You use saveAsTextFile() when you want to store output an external file system (like HDFS, local disk) for further use or analysis.
当你希望把结果存储到外部文件系统(如 HDFS、本地磁盘)以便后续使用或分析时,使用 saveAsTextFile()。
Key Differences
关键差异
| Feature / 特性 | Transformations / 转换 | Actions / 动作 |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Define a new RDD from an existing one | Trigger computation and return a result |
| 定义 | 基于已有数据定义并产生新的 RDD | 触发计算并返回结果 |
| Lazy Evaluation | Yes, evaluated lazily | No, they trigger the actual execution |
| 惰性求值 | 是,惰性执行 | 否,会触发实际执行 |
| Return Type | Returns a new RDD | Returns a value or exports data (to file, driver, etc.) |
| 返回类型 | 返回一个新的 RDD | 返回一个值或将数据导出(文件、Driver 等) |
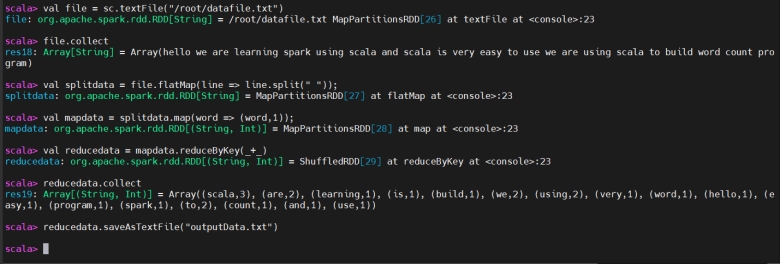
Wordcount Program using spark-shell (Batch Processing)
使用 spark-shell 的词频统计程序(批处理)
Wordcount program using spark-shell
使用 spark-shell 编写的词频统计程序
Create Application using Idea
使用 IDEA 创建应用
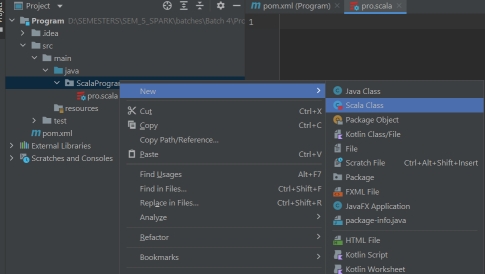
Create new project
创建新项目
- File -> New ->Project
- File -> New -> Project(新建项目)
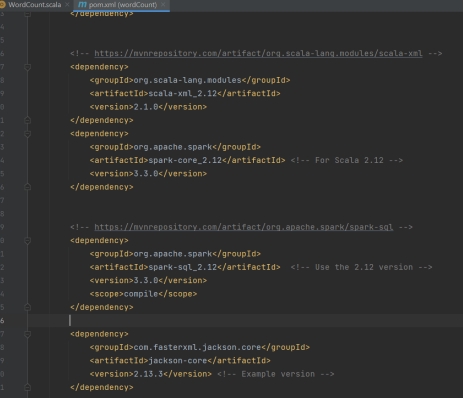
- Add dependencies in pom.xml file
- 在 pom.xml 中添加依赖
- Create package and Object in scala.
- 在 Scala 中创建包与对象(Object)。
- Create File
- 新建文件
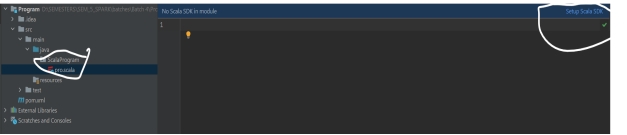
- Setup Scala
- 配置 Scala
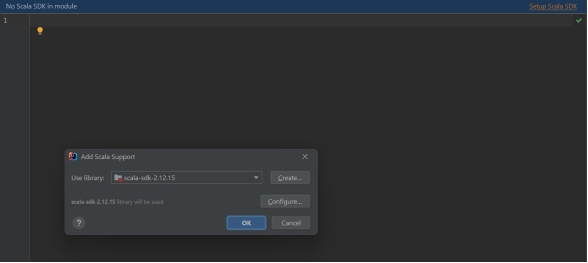
- Now we are ready for scala Application
- 现在可以编写 Scala 应用了
Dependencies in pom.xml file
pom.xml 中的依赖
Dependencies
依赖说明
Scala-lang: This includes the core Scala language library, which is essential for running any Scala code.
Scala-lang: 包含 Scala 语言核心库,运行任何 Scala 代码都必需。
Scala-xml: This library is used for parsing, creating, and manipulating XML data in Scala.
Scala-xml: 用于在 Scala 中解析、创建和操作 XML 数据。
1 | <dependencies> |
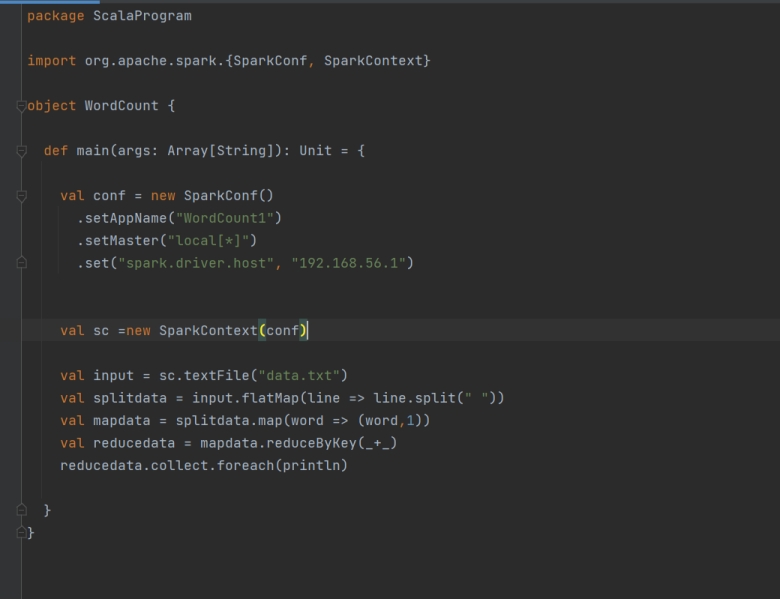
Spark Application using SparkContext
使用 SparkContext 的 Spark 应用
A SparkContext is created by using the SparkConf configuration object.
SparkContext 通过 SparkConf 配置对象创建。
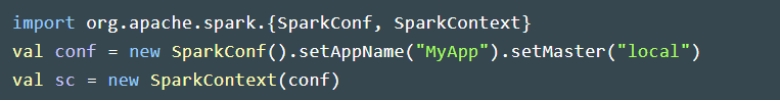
The setAppName() method sets the name of the Spark application, which is useful for monitoring and debugging purposes.
setAppName() 用于设置 Spark 应用名称,便于监控与调试。
The setMaster() method sets the master URL, which is the URL of the cluster manager that the Spark application will connect to. It can be set to “local” to run the application on a single machine, or to the URL of a cluster manager such as Mesos or YARN.
setMaster() 用于设置 Master URL(应用要连接的集群管理器地址)。可设为 “local” 在单机运行,或设为 Mesos/YARN 等集群管理器的地址。
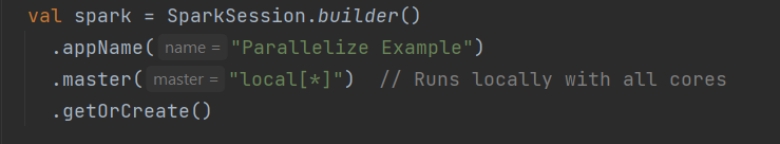
Spark Application using SparkSession
使用 SparkSession 的 Spark 应用
Run Spark Application in Spark-Cluster
在 Spark 集群上运行应用
- Run spark master and worker.
- 启动 Spark Master 与 Worker。
1 | sbin/start-all.sh |
- Spark Master Web UI:
linuxIP:8080 - Spark Master Web UI:
linuxIP:8080 - Spark Master Address:
linuxIP: 7077 - Spark Master 地址:
linuxIP:7077
2 ways to create jar file
创建 JAR 文件的两种方式
Using artifacts
使用 Artifacts
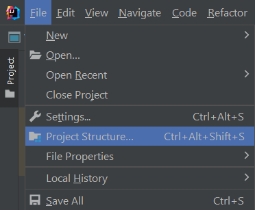
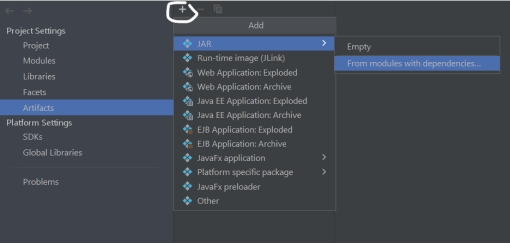
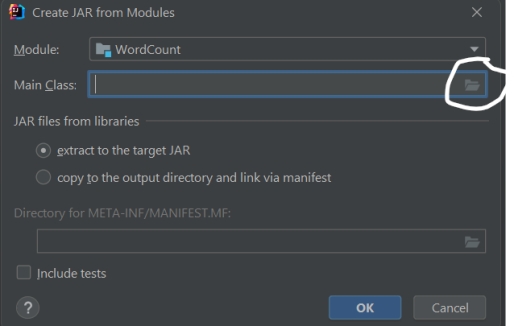
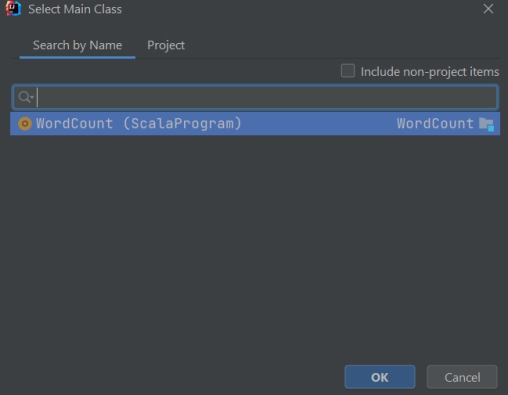
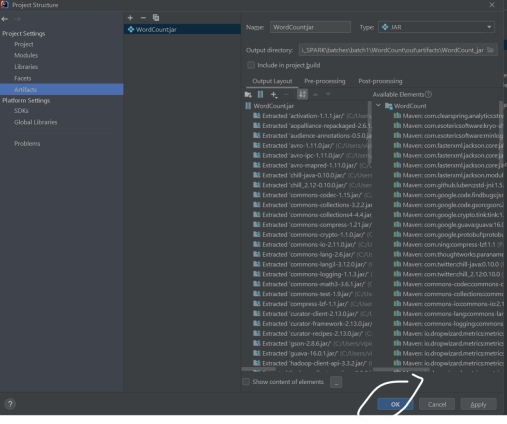
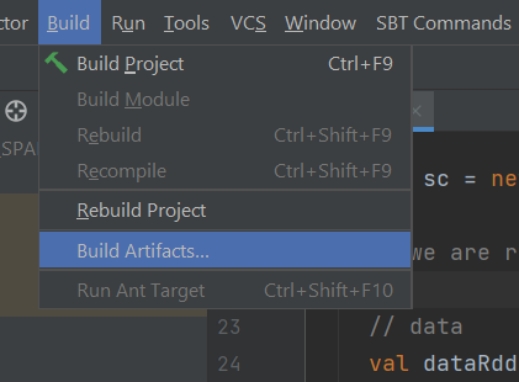
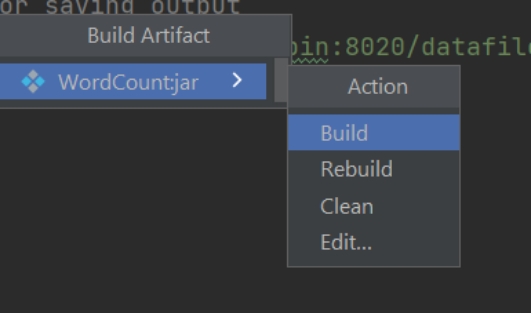
Jar file will create in out directory.
JAR 文件会生成在 out 目录下。
Create jar file using maven-lifecycle
使用 Maven Lifecycle 打包 JAR
Select Maven -> Lifecycle -> clean
选择 Maven -> Lifecycle -> clean
Select Maven -> Lifecycle -> Install
选择 Maven -> Lifecycle -> install
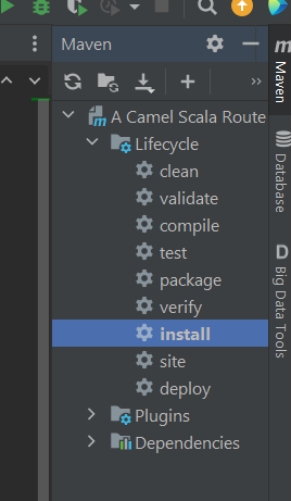
Jar file will create in target directory.
JAR 文件会生成在 target 目录下。
Upload jar file in Linux machine
将 JAR 文件上传到 Linux 机器
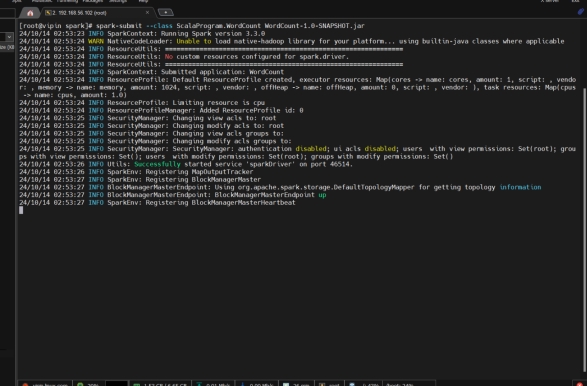
Run spark-submit command to submit application.
使用 spark-submit 提交应用