Chapter 1
第1章
Spark Background
Spark 背景
Although MapReduce is suitable for most batch processing work and becomes the preferred technology for enterprise big data processing in the era of big data, its limitations prompt Spark.
虽然 MapReduce 适用于大多数批处理工作,并且成为大数据时代企业大数据处理的首选技术,但其局限性促使了 Spark 的诞生。
MapReduce gave Spark its background:
MapReduce 为 Spark 提供了背景:
- Programming: MapReduce only provides Map and Reduce methods for processing data, while Spark provides more than 80
- 编程 (Programming):MapReduce 仅提供 Map 和 Reduce 方法来处理数据,而 Spark 提供了超过 80 种方法。
- Task level: Each Map task and Reduce task in MapReduce is a process, which takes a lot of time to start and destroy. Spark’s Tasks are thread-based, with a thread pool within each Executor.
- 任务级别 (Task level):MapReduce 中的每个 Map 任务和 Reduce 任务都是一个进程,启动和销毁需要大量时间。Spark 的任务是基于线程的,每个 Executor 内部都有一个线程池。
- Resource application: In MapReduce, the Maptask and Reducetask of each Job require separate application resources, and repeated application of resources is time-consuming. In Spark, no matter how many jobs an application has, you only need to apply for resources once.
- 资源申请 (Resource application):在 MapReduce 中,每个 Job 的 Map 任务和 Reduce 任务都需要单独申请资源,重复申请资源非常耗时。在 Spark 中,无论一个应用程序有多少个作业,只需要申请一次资源。
- IO: MapReduce is disk-based, Spark is memory-based (Spark is primarily memory-based but can spill to disk when memory is full.). So, there’s a difference in IO.
- IO:MapReduce 是基于磁盘的,Spark 是基于内存的(Spark 主要基于内存,但在内存已满时可以溢出到磁盘)。因此,IO 方面存在差异。
- Sorting: In the execution process of MapReduce, sorting is also an expensive operation. Some businesses do not need sorting. To avoid sorting, open bypass mechanism in Spark.
- 排序 (Sorting):在 MapReduce 的执行过程中,排序也是一项昂贵的操作。有些业务不需要排序。为了避免排序,Spark 中开启了旁路机制 (bypass mechanism)。
- Iterative processing: MapReduce’s iterative processing is disk-based, with each job completing the data drop, the next job disk reading the file and processing, and the connection between jobs requiring programmer intervention (please ignore one Hive SQL multiple jobs). Spark iteration processing is based on memory, and jobs can be executed in tandem in memory, with one job completing followed by the next.
- 迭代处理 (Iterative processing):MapReduce 的迭代处理是基于磁盘的,每个作业完成后数据落盘,下一个作业从磁盘读取文件并处理,作业之间的连接需要程序员干预(请忽略 Hive SQL 的多作业情况)。Spark 的迭代处理是基于内存的,作业可以在内存中串行执行,一个作业完成后紧接着执行下一个。
Spark History
Spark 历史
The Spark was initiated by Matei Zaharia at UC Berkeley’s AMPLab in 2009. It was open sourced in 2010 under a BSD license. Spark 由 Matei Zaharia 于 2009 年在加州大学伯克利分校的 AMPLab 发起。它于 2010 年开源,采用 BSD 许可证。
In 2013, the project was acquired by Apache Software Foundation. In 2014, the Spark emerged as a Top-Level Apache Project. 2013 年,该项目被 Apache 软件基金会收购。2014 年,Spark 成为 Apache 顶级项目。
Key Features of Apache Spark:
Apache Spark 的主要特性:
1. Speed:
1. 速度:
- In-memory Computing: Spark processes data in memory (RAM), which significantly speeds up data processing tasks.
- 内存计算 (In-memory Computing):Spark 在内存 (RAM) 中处理数据,这显著加快了数据处理任务的速度。
- Optimized Execution: Spark uses directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) to optimize execution plans for data processing.
- 优化执行 (Optimized Execution):Spark 使用有向无环图 (DAG) 来优化数据处理的执行计划。
2. Ease of Use:
2. 易用性:
- APIs: Spark provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, Python, and R, making it accessible to a wide range of developers.
- API:Spark 提供了 Java、Scala、Python 和 R 的高级 API,使广大开发者都能使用它。
- Interactive Shells: Spark supports interactive shells for Python (PySpark) and Scala, allowing for interactive data analysis.
- 交互式 Shell (Interactive Shells):Spark 支持 Python (PySpark) 和 Scala 的交互式 Shell,允许进行交互式数据分析。
3. General-purpose:
3. 通用性:
- Libraries: Spark includes libraries for SQL (Spark SQL), streaming data (Spark Streaming), machine learning (MLlib), and graph processing (GraphX).
- 库 (Libraries):Spark 包含了用于 SQL (Spark SQL)、流数据 (Spark Streaming)、机器学习 (MLlib) 和图处理 (GraphX) 的库。
4. Compatibility:
4. 兼容性:
- Hadoop Integration: Spark can read from and write to HDFS, and it integrates well with the Hadoop ecosystem.
- Hadoop 集成:Spark 可以从 HDFS 读取和写入数据,并且与 Hadoop 生态系统集成良好。
- Data Sources: Spark can process data from various sources, including HDFS, Apache HBase, Apache Cassandra, Amazon S3, and more.
- 数据源:Spark 可以处理来自各种来源的数据,包括 HDFS、Apache HBase、Apache Cassandra、Amazon S3 等。
Streaming-Oriented Computation
面向流的计算
Streaming-oriented computation in Apache Spark refers to the ability to process and analyze data streams in real-time using Spark’s streaming capabilities.
Apache Spark 中的面向流计算指的是利用 Spark 的流处理能力实时处理和分析数据流的能力。
Data as a whole can be divided into static data and stream data. The processing of static data and stream data corresponds to two distinct computing modes: batch computing and real-time.
数据整体上可以分为 静态数据和流数据。静态数据和流数据的处理对应着两种截然不同的计算模式:批量计算和实时计算。
In general, streaming computing adheres to the basic idea that the value of data decreases over time. Therefore, when an event occurs, it should be processed immediately, rather than cached for bulk processing.
一般来说,流计算遵循的基本理念是数据的价值随时间递减。因此,当事件发生时,应立即处理,而不是缓存起来进行批量处理。
For a streaming computing system, it should meet the following requirements:
对于一个流计算系统,它应该满足以下要求:
- High performance: It is the basic requirements for processing big data, which requires the system can process hundreds of thousands of data per second.
- 高性能 (High performance):这是处理大数据的基本要求,要求系统每秒能处理数十万条数据。
- Massive scale: Support terabytes or even petabytes of data size.
- 海量规模 (Massive scale):支持 TB 甚至 PB 级的数据规模。
- Real-time: A low latency must be guaranteed, reaching the level of seconds or even milliseconds.
- 实时性 (Real-time):必须保证低延迟,达到秒级甚至毫秒级。
- Distributed: A basic architecture that supports big data and must be able to scale smoothly.
- 分布式 (Distributed):支持大数据的基本架构,必须能够平滑扩展。
- Ease of use: Rapid development and deployment.
- 易用性 (Ease of use):快速开发和部署。
- Reliability: Ability to process streaming data reliably
- 可靠性:能够可靠地处理流数据
Spark Ecosphere
Spark 生态圈
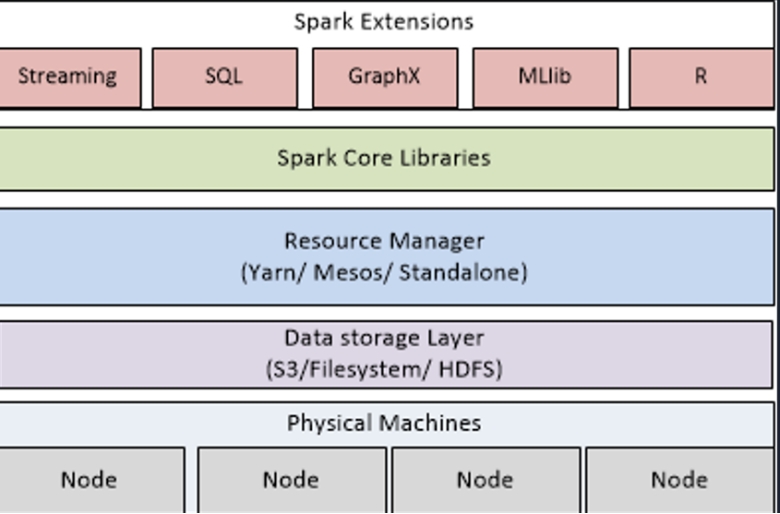
Architecture of Spark
Spark 架构
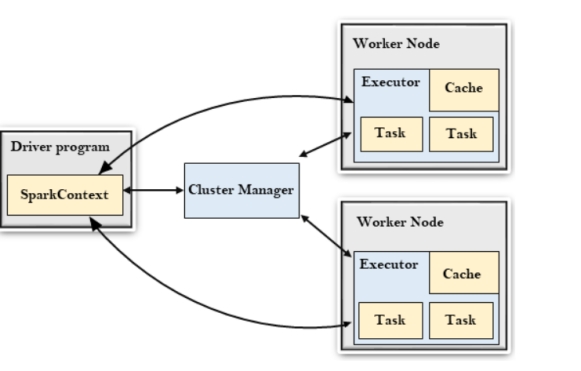
Core Components of Spark Architecture
Spark 架构的核心组件
Spark has master and slave architecture. The master is called the Driver Node, and the workers are called Worker Nodes.
Spark 采用主从 (Master-Slave) 架构。主节点称为驱动器节点 (Driver Node),工作节点称为工作者节点 (Worker Nodes)。
1. Driver Program
1. 驱动程序 (Driver Program)
- Role: The driver program is the master node in Spark. It is responsible for converting the user’s code into a directed acyclic graph (DAG) of stages and tasks. It schedules tasks and distributes them across the cluster.
- 角色:驱动程序是 Spark 中的主节点。它负责将用户的代码转换为由阶段 (Stages) 和任务 (Tasks) 组成的有向无环图 (DAG)。它调度任务并将其分发到整个集群。
- Responsibilities:
- 职责:
- Converting user-defined transformations and actions into a DAG.
- 将用户定义的转换 (Transformations) 和动作 (Actions) 转换为 DAG。
- Scheduling tasks to be executed on worker nodes.
- 调度任务以便在工作节点上执行。
- Distributing tasks to executors.
- 将任务分发给执行器 (Executors)。
- Collecting and aggregating results from executors.
- 收集并聚合来自执行器的结果。
- Handling failures and retries.
- 处理故障和重试。
2. Cluster Manager
2. 集群管理器 (Cluster Manager)
- Role: The cluster manager allocates resources across the cluster. Spark supports several types of cluster managers:
- 角色:集群管理器在集群中分配资源。Spark 支持几种类型的集群管理器:
- Standalone Cluster Manager: Comes built-in with Spark.
- 独立集群管理器 (Standalone Cluster Manager):Spark 内置。
- Apache Mesos: A general-purpose cluster manager.
- Apache Mesos:通用的集群管理器。
- Hadoop YARN: The resource manager used in Hadoop.
- Hadoop YARN:Hadoop 中使用的资源管理器。
- Kubernetes: An open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- Kubernetes:用于自动化部署、扩展和管理容器化应用程序的开源系统。
- Responsibilities:
- 职责:
- Allocating resources (CPU, memory) to Spark applications.
- 为 Spark 应用程序分配资源(CPU、内存)。
- Managing the lifecycle of Spark applications.
- 管理 Spark 应用程序的生命周期。
3. Executors
3. 执行器 (Executors)
- Role: Executors are worker nodes that perform the actual computations. Each Spark application has its own set of executors.
- 角色:执行器是执行实际计算的工作节点。每个 Spark 应用程序都有自己的一组执行器。
- Responsibilities:
- 职责:
- Executing tasks assigned by the driver.
- 执行驱动器分配的任务。
- Storing data in memory or on disk (caching).
- 将数据存储在内存或磁盘中(缓存)。
- Communicating results back to the driver.
- 将结果传回驱动器。
- Handling data shuffling between nodes as required by the task.
- 根据任务需要处理节点之间的数据混洗 (Shuffling)。
4. Tasks
4. 任务 (Tasks)
- Role: Tasks are units of work that are sent to executors by the driver.
- 角色:任务是驱动器发送给执行器的工作单元。
- Responsibilities:
- 职责:
- Performing operations (transformations) on data.
- 对数据执行操作(转换)。
- Reading and writing data from and to HDFS, S3, or other data sources.
- 从 HDFS、S3 或其他数据源读取和写入数据。
Working
工作原理
- The user submits a Spark application (a driver program) to the cluster.
- 用户向集群提交 Spark 应用程序(驱动程序)。
- The driver program translates the user’s code into a DAG of stages. Each stage consists of tasks that can be executed in parallel.
- 驱动程序将用户的代码转换为阶段的 DAG。每个阶段包含可以并行执行的任务。
- The driver requests resources from the cluster manager.
- 驱动器向集群管理器请求资源。
- Once resources are allocated, the driver schedules tasks to be executed on available executors. Executors execute the tasks, performing the necessary transformations and actions on the data. Intermediate data can be stored in memory or on disk to speed up subsequent operations.
- 一旦分配了资源,驱动器就会调度任务在可用的执行器上执行。执行器执行任务,对数据执行必要的转换和动作。中间数据可以存储在内存或磁盘中,以加速后续操作。
Spark Core components
Spark 核心组件
Spark Core:
Spark Core(核心):
The foundation of the Spark framework, responsible for memory management, task scheduling, fault recovery, and interaction with storage systems.
Spark 框架的基础,负责内存管理、任务调度、故障恢复以及与存储系统的交互。
Spark SQL:
Spark SQL:
A module for structured data processing. It allows querying data via SQL and supports data sources such as Hive, Avro, Parquet, ORC, and JSON.
用于结构化数据处理的模块。它允许通过 SQL 查询数据,并支持 Hive、Avro、Parquet、ORC 和 JSON 等数据源。
Spark Streaming:
Spark Streaming:
Enables real-time stream processing. It can ingest data streams from sources like Apache Kafka, Flume, and Kinesis, and process them using complex algorithms expressed with high-level functions.
实现实时流处理。它可以从 Apache Kafka、Flume 和 Kinesis 等源摄取数据流,并使用高级函数表达的复杂算法对其进行处理。
MLlib:
MLlib:
Spark’s scalable machine learning library, which includes algorithms for classification, regression, clustering, collaborative filtering, and more.
Spark 的可扩展机器学习库,其中包括用于分类、回归、聚类、协同过滤等的算法。
GraphX:
GraphX:
A library for graph processing and analysis. It provides an API for graph operations and algorithms like PageRank.
用于图处理和分析的库。它提供了用于图操作和算法(如 PageRank)的 API。
Advantage of spark
Spark 的优势
- Spark processes data in memory, which can significantly speed up computations compared to disk-based systems like Hadoop MapReduce. This is especially beneficial for iterative algorithms and interactive data analysis.
- Spark 在内存中处理数据,与 Hadoop MapReduce 等基于磁盘的系统相比,可以显著加快计算速度。这对于迭代算法和交互式数据分析特别有益。
- Spark provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, Python, and R, making it accessible to a wide range of developers.
- Spark 提供了 Java、Scala、Python 和 R 的高级 API,使广大开发者都能使用它。
- Spark supports batch processing, real-time streaming, machine learning, and graph processing within a single framework, reducing the need to use multiple tools.
- Spark 在单个框架内支持批处理、实时流处理、机器学习和图处理,减少了使用多种工具的需求。
- Spark can scale from a single machine to thousands of cluster nodes, making it suitable for handling large datasets.
- Spark 可以从单台机器扩展到数千个集群节点,使其适合处理大型数据集。
- Spark includes libraries for SQL and structured data processing (Spark SQL), machine learning (MLlib), graph processing (GraphX), and stream processing (Spark Streaming and Structured Streaming).
- Spark 包含了用于 SQL 和结构化数据处理 (Spark SQL)、机器学习 (MLlib)、图处理 (GraphX) 以及流处理 (Spark Streaming 和 Structured Streaming) 的库。
Disadvantage of spark
Spark 的劣势
- High Memory Usage: Spark’s in-memory processing can consume a large amount of memory, which can be expensive and may lead to issues if not managed properly.
- 高内存占用 (High Memory Usage):Spark 的内存处理可能会消耗大量内存,这可能很昂贵,如果管理不当可能会导致问题。
- Garbage Collection Overhead: In-memory storage can lead to increased garbage collection overhead in the JVM, affecting performance.
- 垃圾回收开销 (Garbage Collection Overhead):内存存储会导致 JVM 中的垃圾回收开销增加,从而影响性能。
- Running Spark on a large cluster can be expensive due to the high memory and CPU requirements.
- 由于对内存和 CPU 的要求很高,在大型集群上运行 Spark 可能会很昂贵。
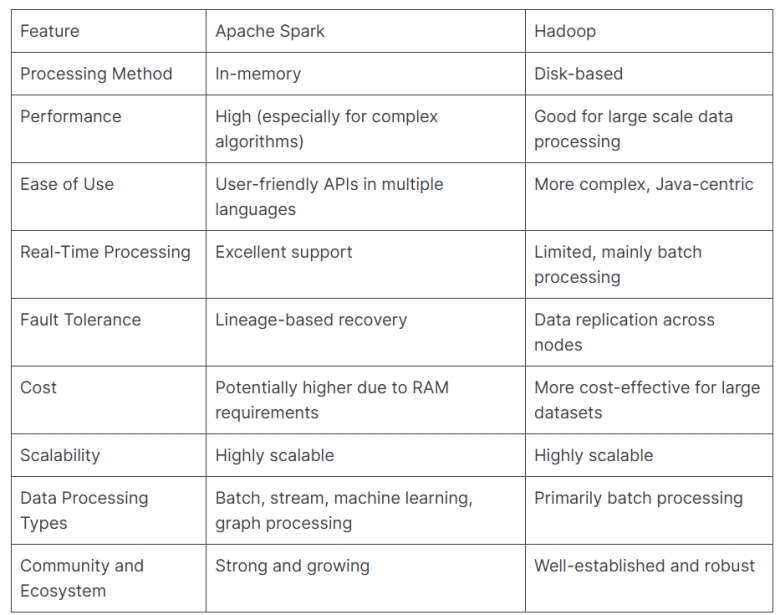
Spark vs Hadoop
Spark 对比 Hadoop