Chapter 1
Big Data is a collection of data that is huge in volume, yet growing exponentially with time.
大数据是一个数据量巨大且随时间指数级增长的数据集合。
Big data is also a data but with huge size.
大数据也是数据,但具有巨大的规模。
There are 3 types of Big data:
大数据有三种类型:
Structured: Any data that can be stored, accessed and processed in the form of fixed format is termed as a ‘structured’ data.
结构化数据: 任何能够以固定格式存储、访问和处理的数据被称为”结构化”数据。
- Ex. RDBMS data
- 例如:关系数据库管理系统数据
Unstructured: Any data with unknown form or the structure is classified as unstructured data.
非结构化数据: 任何形式或结构未知的数据都被归类为非结构化数据。
- Ex. Images, Audio and Video files.
- 例如:图像、音频和视频文件。
Semi-structured: Semi-structured data can contain both the forms of data.
半结构化数据: 半结构化数据可以包含两种形式的数据。
- We can see semi-structured data as a structured in form but it is actually not defined with e.g. a table definition in relational DBMS.
- 我们可以看到半结构化数据在形式上是结构化的,但实际上并没有像关系数据库管理系统中的表定义那样被定义。
- Ex. JSON, XML file.
- 例如:JSON、XML文件。
Big data can be described by the following characteristics
大数据可以通过以下特征来描述
Volume – Volume refers to the size of the data which is enormous.
数据量 – 数据量是指数据的规模,这是巨大的。
- The size of data plays a very crucial role in determining its value out of data.
- 数据的大小在确定数据价值方面起着非常关键的作用。
Variety – Variety refers to heterogeneous sources and the nature of data, both structured and unstructured.
多样性 – 多样性是指异构数据源和数据的性质,包括结构化和非结构化数据。
Velocity – The term ‘velocity’ refers to the speed of generation of data.
速度 – “速度”一词是指数据生成的速度。
- How fast the data is generated and processed to meet the demands, determines real potential in the data.
- 数据生成和处理的速度如何满足需求,决定了数据的真正潜力。
Veracity – Veracity is about the content quality that should be analysed.
真实性 – 真实性是指应该分析的内容质量。
- High-veracity data provide information that is valuable to analyse, while low-veracity data contains a lot of empty figures widely known as noise.
- 高真实性数据提供有价值的分析信息,而低真实性数据包含大量空白数据,通常被称为噪声。
Advantages Of Big Data Processing
大数据处理的优势
Businesses can utilize outside intelligence while taking decisions
企业在做决策时可以利用外部智能
Improved customer service
改善客户服务
Early identification of risk to the product/services, if any.
早期识别产品/服务的风险(如果有的话)。
Better operational efficiency
更好的运营效率
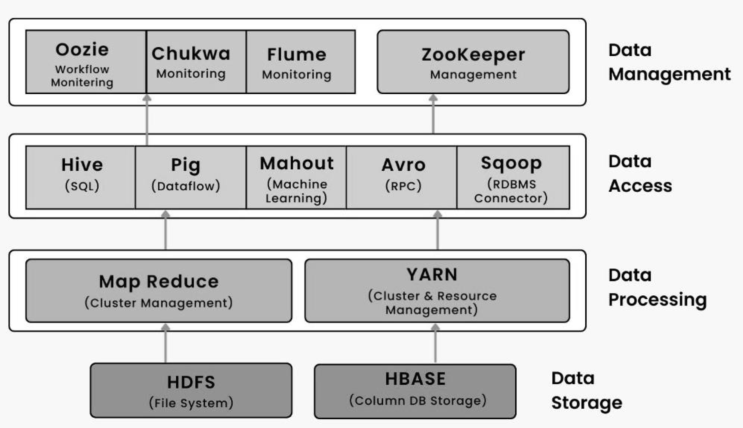
The tools of Hadoop ecosystem are as below
Hadoop生态系统的工具如下
HBase
HBase is an open-source, non-relational distributed database.
HBase是一个开源的、非关系型分布式数据库。
In other words, it is a NoSQL database.
换句话说,它是一个NoSQL数据库。
The HBase was designed to run on top of HDFS and provides BigTable-like capabilities.
HBase被设计为在HDFS之上运行,并提供类似BigTable的功能。
The HBase is written in Java, whereas HBase applications can be written in REST, Avro, and Thrift APIs.
HBase是用Java编写的,而HBase应用程序可以使用REST、Avro和Thrift API编写。
HIVE
HIVE provides a range of tools to ==extract/transform/load data (ETL)==.
HIVE提供一系列工具来==提取/转换/加载数据(ETL)==。
HIVE can store, query, and analyze large-scale data stored in HDFS (or HBase).
HIVE可以存储、查询和分析存储在HDFS(或HBase)中的大规模数据。
Hive defines a query language similar to SQL, called ==HQL==.
Hive定义了一种类似SQL的查询语言,称为==HQL==。
Converts ==unstructured data== into ==structured data==
将==非结构化数据==转换为==结构化数据==
Disadvantages of Hive:
Hive的缺点:
Hive does not currently support transactions
Hive目前不支持事务
Cannot modify table data (cannot update, delete, insert)
不能修改表数据(不能更新、删除、插入)
Slow query speed
查询速度慢
STORM
Apache Storm is a free, open source distributed real-time computing system that simplifies the reliable processing of streaming data.
Apache Storm是一个免费的、开源的分布式实时计算系统,简化了流数据的可靠处理。
Apache Storm features are:
Apache Storm的特点是:
Easy to expand
易于扩展
Fault tolerance
容错性
Low Latency
低延迟
Zookeeper
- Apache Zookeeper is the coordinator of any Hadoop job which includes a combination of various services in a Hadoop Ecosystem.
- Apache Zookeeper是任何Hadoop作业的协调器,它包括Hadoop生态系统中各种服务的组合。
SQOOP
- Sqoop allows users to extract data from relational databases into Hadoop for further processing.
- Sqoop允许用户从关系数据库中提取数据到Hadoop中进行进一步处理。
Criteria to Evaluate Distribution
评估分布的标准
Performance
性能
Scalability
可扩展性
Reliability
可靠性
Chapter 2
The main modes of Hadoop operation:
Hadoop操作的主要模式:
Local runtime mode
本地运行模式
- By default, Hadoop will run in a non-distributed mode as a single Java process, there are ==no daemons== to run in this mode
- 默认情况下,Hadoop将以非分布式模式作为单个Java进程运行,在此模式下==没有守护进程==运行
- This mode is suitable for use during the ==development phase==.
- 此模式适合在==开发阶段==使用。
Pseudo-distributed operating mode
伪分布式操作模式
- Hadoop can run on a single node, with each Hadoop daemon running in a separate Java process in a Mode called pseudo-distributed Mode.
- Hadoop可以在单个节点上运行,每个Hadoop守护进程在称为伪分布式模式的模式中以单独的Java进程运行。
- This mode is often used in the ==experimental learning phase==.
- 此模式通常在==实验学习阶段==使用。
- The process names are as follows:
- 进程名称如下:
NameNode
DataNode
SecondaryNameNode
ResourceManager
NodeManager
Fully distributed operating mode
完全分布式操作模式
Hadoop runs on a cluster where each Hadoop daemon runs in Java processes on each server node in the cluster.
Hadoop运行在集群上,其中每个Hadoop守护进程在集群中每个服务器节点上的Java进程中运行。
This mode is often used in the stage of ==experimental verification and enterprise commissioning==.
此模式通常用于==实验验证和企业调试==阶段。
The process names are as follows:
进程名称如下:
NameNode
DataNode
SecondaryNameNode
ResourceManager
NodeManager
HDFS Daemon Process
HDFS守护进程
HDFS (distributed file system) is used to solve the problem of storing large amounts of data.
HDFS(分布式文件系统)用于解决存储大量数据的问题。
The
NameNode,DataNode, andSecondaryNameNodeprocesses are required for the normal operation of the HDFS.NameNode、DataNode和SecondaryNameNode进程是HDFS正常操作所必需的。start-dfs.shcommand to start the HDFS daemon process to provide external servicesstart-dfs.sh命令启动HDFS守护进程以提供外部服务
Yarn Daemon Process
Yarn守护进程
YARN is the resource management system in ==Hadoop 3.x==.
YARN是==Hadoop 3.x==中的资源管理系统。
The
ResourceManagerandNodeManagerprocesses are required for YARN to work properly.ResourceManager和NodeManager进程是YARN正常工作所必需的。start-yarn.shcommand to start the YARN daemon process to provide services externally.start-yarn.sh命令启动YARN守护进程以对外提供服务。
Pattern Configuration
模式配置
core-site.xml: In pseudo-distributed mode, you only need to configure the
NameNodeRPC remote communication address and port number.core-site.xml:在伪分布式模式下,只需要配置
NameNodeRPC远程通信地址和端口号。- The property name is
fs.defaultFSand the default port number is 8020. - 属性名称是
fs.defaultFS,默认端口号是8020。
- The property name is
hdfs-site.xml: In pseudo-distributed mode, you only need to set the number of data block copies to 1.
hdfs-site.xml:在伪分布式模式下,只需要将数据块副本数设置为1。
- The property name is
dfs.replication. - 属性名称是
dfs.replication。
- The property name is
mapred-site.xml: In pseudo-distributed mode, you only need to set the MapReduce operating framework to YARN.
mapred-site.xml:在伪分布式模式下,只需要将MapReduce操作框架设置为YARN。
- The property name is
mapreduce.framework.name. - 属性名称是
mapreduce.framework.name。
- The property name is
yarn-site.xml: In pseudo-distributed mode, only the
ResourceManagercommunication address and aux-services of theNodeManagerneed to be configured.yarn-site.xml:在伪分布式模式下,只需要配置
ResourceManager通信地址和NodeManager的辅助服务。- The name of properties are:
yarn.ResourceManager.hostnameandyarn.NodeManager.aux-services. - 属性名称是:
yarn.ResourceManager.hostname和yarn.NodeManager.aux-services。
- The name of properties are:
HDFS HA Architecture
HDFS高可用架构
The concept of High Availability cluster was introduced in ==Hadoop 2.x== to solve the single point of failure problem in Hadoop 1.x.
高可用集群的概念在==Hadoop 2.x==中引入,以解决Hadoop 1.x中的单点故障问题。
The HA architecture solved this problem of
NameNodeavailability by allowing us to have twoNameNodes in an ==active/passive== configuration.HA架构通过允许我们在==主动/被动==配置中拥有两个
NameNode来解决NameNode可用性问题。If one
NameNodegoes down, the otherNameNodecan take over the responsibility and therefore, reduce the cluster down time.如果一个
NameNode宕机,另一个NameNode可以接管责任,从而减少集群停机时间。There are two issues in maintaining consistency in the HDFS High Availability cluster:
在维护HDFS高可用集群一致性方面有两个问题:
Active and
Standby NameNodeshould always be in sync with each other.活动和备用
NameNode应该始终保持同步。There should be only one
Active NameNodeat a time because twoActive NameNodewill lead to corruption of the data.一次只能有一个活动的
NameNode,因为两个活动的NameNode会导致数据损坏。
Implementation of HA Architecture
HA架构的实现
- In HDFS HA Architecture, we have two
NameNodes running at the same time. - 在HDFS HA架构中,我们有两个
NameNode同时运行。 - So, we can implement the Active and
Standby NameNodeconfiguration in the following two ways: - 所以,我们可以通过以下两种方式实现主备
NameNode配置:
Using Quorum Journal Nodes
使用仲裁日志节点
The
Standby NameNodeand theActive NameNodekeep in sync with each other through a separate group of nodes or daemons -called JournalNodes.备用
NameNode和活动NameNode通过一个单独的节点组或守护进程——称为JournalNodes——保持彼此同步。The
Active NameNodeis responsible for updating the EditLogs present in the JournalNodes.活动
NameNode负责更新JournalNodes中存在的EditLogs。The
StandbyNodereads the changes made to the EditLogs in the JournalNode and applies it to its own namespace in a constant manner.StandbyNode读取JournalNode中对EditLogs所做的更改,并以持续的方式将其应用到自己的命名空间。During failover, the
StandbyNodemakes sure that it has updated its metadata information from the JournalNodes before becoming the newActive NameNode在故障转移期间,
StandbyNode确保在成为新的活动NameNode之前已从JournalNodes更新了其元数据信息
Using Shared Storage
使用共享存储
The
StandbyNodeand theActive NameNodekeep in sync with each other by using a shared storage device.StandbyNode和活动NameNode通过使用共享存储设备保持彼此同步。The
Active NameNodelogs the record of any modification done in its namespace to an EditLog present in this shared storage.活动
NameNode将其命名空间中所做的任何修改记录记录到此共享存储中存在的EditLog中。The
StandbyNodereads the changes made to the EditLogs in this shared storage and applies it to its own namespace.StandbyNode读取此共享存储中对EditLogs所做的更改,并将其应用到自己的命名空间。During failover, the
StandbyNodemakes sure that it has updated its metadata information from the shared storage before becoming the newActive NameNode在故障转移期间,
StandbyNode确保在成为新的活动NameNode之前已从共享存储更新了其元数据信息
Hadoop Authority Management
Hadoop权限管理
1 | <property> |
hadoop.security.authorization=trueproperty incore-site.xmlfile turns on ServiceLevel Authorization.core-site.xml文件中的hadoop.security.authorization=true属性开启服务级别授权。- If it is false, it does not pass any verification.
- 如果为false,则不通过任何验证。
Hadoop Ecosystem is neither a programming language nor a service, it is a ==platform or framework== which solves big data problems.
Hadoop生态系统既不是编程语言也不是服务,它是一个解决大数据问题的==平台或框架==。
- You can consider it as a suite which encompasses a number of services (ingesting, storing, analyzing and maintaining) inside it.
- 您可以将其视为一个包含多个服务(摄取、存储、分析和维护)的套件。
Chapter 3
The HDFS comprises the following components:
HDFS包含以下组件:
NameNode(Master Node): The Name Node is the centralized piece of the HDFS.NameNode(主节点):NameNode是HDFS的中心化组件。- It is known as the Master and it is designed to store the Meta Data.
- 它被称为主节点,用于存储元数据。
NameNodeis responsible for monitoring the Health Status of the Slave Nodes and assigning Tasks to the Data Nodes.NameNode负责监控从节点的健康状态并向数据节点分配任务。
Secondary
NameNode: It acts as a ==Buffer== to the Name Node.辅助
NameNode: 它充当NameNode的==缓冲区==。- It stores the intermediate updates the FS-image of the Name Node in the Edit-log and updates the information to the Final FS-image when the name node is inactive.
- 它存储
NameNode的FS映像的中间更新到编辑日志中,并在NameNode不活动时将信息更新到最终FS映像。
Data Node: Data Node is the actual unit which stores the data.
数据节点: 数据节点是实际存储数据的单元。
- It is known as the Slave and it responds to the Name Node about its Health Status and the task status in the form of a ==Heartbeat==.
- 它被称为从节点,以==心跳==的形式向
NameNode报告其健康状态和任务状态。
Block in HDFS
HDFS中的块
- Block is the smallest unit of storage on a computer system.
- 块是计算机系统上存储的最小单位。
- It is the smallest contiguous storage allocated to a file.
- 它是分配给文件的最小连续存储。
- In Hadoop, we have a default block size of 128MB.
- 在Hadoop中,我们有一个默认的128MB块大小。
Replication Management
副本管理
HDFS uses a ==replica== process to handle faults.
HDFS使用==副本==过程来处理故障。
Replication factor decides how many copies of the blocks get stored.
副本因子决定存储多少块副本。
It is 3 by default but we can configure to any value.
默认为3,但我们可以配置为任何值。
Replications operate under two rules: Two identical blocks cannot be placed on the same
DataNode.副本在两个规则下运行:两个相同的块不能放在同一个
DataNode上。When a cluster is rack aware, all the replicas of a block cannot be placed on the same rack.
当集群具有机架感知时,一个块的所有副本不能放在同一个机架上。
Advantages of HDFS
HDFS的优势
Data is highly fault-tolerant
数据具有高容错性
They are suitable for processing Big Data,
它们适合处理大数据,
Supports streamed data retrieval, ensuring data consistency
支持流式数据检索,确保数据一致性
Can be built on low-cost machines to improve reliability using a multicast mechanism
可以建立在低成本机器上,使用组播机制提高可靠性
Disadvantages of HDFS
HDFS的缺点
HDFS is not efficient to store a large number of ==small files==
HDFS在存储大量==小文件==方面效率不高
HDFS is not good for ==low-latency== data access
HDFS不适合==低延迟==数据访问
They do not support ==concurrent writing== and ==random file modification==
它们不支持==并发写入==和==随机文件修改==
Why YARN?
为什么要YARN?
- MapReduce performed both processing and resource management functions in Hadoop version 1.0 and has only HDFS, MapReduce & common modules while Hadoop version 2.0 also has YARN module.
- MapReduce在Hadoop 1.0版本中同时执行处理和资源管理功能,只有HDFS、MapReduce和通用模块,而Hadoop 2.0版本还有YARN模块。
YARN Core Components
YARN核心组件
The elements of YARN include:
YARN的元素包括:
ResourceManager(one per cluster)ResourceManager(每个集群一个)ApplicationMaster(one per application)ApplicationMaster(每个应用程序一个)NodeManagers(one per node)NodeManagers(每个节点一个)Container
容器
NodeManager(NM): NM monitor the resource usage by the container and sends signals (heartbeats) to ResourceManger.NodeManager(NM): NM监控容器的资源使用情况,并向ResourceManger发送信号(心跳)。- The resources are like CPU, memory, disk, network and so on.
- 资源包括CPU、内存、磁盘、网络等。
ApplicationMaster(AM): AM manages the resource needs of individual applications and interacts with the scheduler to acquire the required resources.ApplicationMaster(AM): AM管理各个应用程序的资源需求,并与调度器交互以获取所需资源。- It connects with the node manager to execute and monitor tasks.
- 它与节点管理器连接以执行和监控任务。
Container: Houses a collection of resources like RAM, CPU, and network bandwidth
容器: 容纳一系列资源,如RAM、CPU和网络带宽
Resource Manager (RM): RM manages the resource allocation in the cluster and is responsible for tracking how many resources are available in the cluster and each node manager’s contribution.It has two main components
资源管理器(RM): RM管理集群中的资源分配,负责跟踪集群中有多少资源可用以及每个节点管理器的贡献。它有两个主要组件
Scheduler: Scheduler is responsible for allocating resources to various running applications and scheduling resources based on the requirements of the application.
调度器: 调度器负责为各种运行的应用程序分配资源,并根据应用程序的要求调度资源。
Application Manager: Accept job submissions from the client or monitor and restart application masters in case of failure.
应用程序管理器: 接受客户端的作业提交,或监控和重启失败的应用程序主节点。
MapReduce
MapReduce
MapReduce is a programming framework that allows us to perform ==distributed and parallel processing== on large data sets in a distributed environment.
MapReduce是一个编程框架,允许我们在分布式环境中对大数据集执行==分布式和并行处理==。
MapReduce consists of two distinct tasks – Map and Reduce.
MapReduce由两个不同的任务组成——Map和Reduce。
MapReduce model has three major phases:
MapReduce模型有三个主要阶段:
Mapper: Mapper function accepts key-value pairs as input as
(k, v), where the key represents the ==offset address== of each record and the value represents the ==entire record content==.映射器: 映射器函数接受键值对作为输入
(k, v),其中键表示每个记录的==偏移地址==,值表示==整个记录内容==。- The output of the Mapper phase will also be in the key-value format as (k’, v’).
- 映射器阶段的输出也将是键值格式
(k', v')。
Shuffle and Sort: The output of various mappers
(k', v'), then goes into Shuffle and Sort phase.洗牌和排序: 各种映射器的输出
(k', v'),然后进入洗牌和排序阶段。- All the duplicate values are removed, and different values are grouped together based on similar keys.
- 所有重复值都被移除,不同的值根据相似的键组合在一起。
- The output of the Shuffle and Sort phase will be key-value pairs again as key and array of values
(k, v[]). - 洗牌和排序阶段的输出将再次是键值对,即键和值数组
(k, v[])。
Reducer: The reducer receives the key-value pair from multiple map jobs.
归约器: 归约器从多个映射作业中接收键值对。
- Then, the reducer aggregates those intermediate data tuples (intermediate key-value pairs) into a key-value pairs which is the final output.
- 然后,归约器将这些中间数据元组(中间键值对)聚合成最终输出的键值对。
Chapter 4
HDFS Commands
HDFS命令
copyFromLocal (or) put: To copy files/folders from local file system to hdfs store.copyFromLocal (or) put:将文件/文件夹从本地文件系统复制到hdfs存储。- Syn:-
hdfs dfs -copyFromLocal <local file path> <dest(present on hdfs)> - 语法:-
hdfs dfs -copyFromLocal <本地文件路径> <目标(hdfs上存在)>
- Syn:-
copyToLocal (or) get: To copy files/folders from hdfs store to local file system.copyToLocal (or) get:将文件/文件夹从hdfs存储复制到本地文件系统。- Syn:-
hdfs dfs -copyToLocal <<srcfile(on hdfs)> <local file dest>> - 语法:-
hdfs dfs -copyToLocal <<源文件(hdfs上)> <本地文件目标>>
- Syn:-
moveFromLocal: This command will move files from local to hdfs.moveFromLocal:此命令将文件从本地移动到hdfs。- Syn:-
hdfs dfs -moveFromLocal <local src> <dest(on hdfs)> - 语法:-
hdfs dfs -moveFromLocal <本地源> <目标(hdfs上)>
- Syn:-
cp: This command is used to copy files within hdfscp:此命令用于在hdfs内复制文件- Syn:-
hdfs dfs -cp <src(on hdfs)> <dest(on hdfs)> - 语法:-
hdfs dfs -cp <源(hdfs上)> <目标(hdfs上)>
- Syn:-
mv: This command is used to move files within hdfs. Let’s cut-paste a file myfile.txt from niit folder to niit_copied.mv:此命令用于在hdfs内移动文件。让我们将文件myfile.txt从niit文件夹剪切粘贴到niit_copied。- Syn:-
hdfs dfs -mv <src(on hdfs)> <src(on hdfs)> - 语法:-
hdfs dfs -mv <源(hdfs上)> <源(hdfs上)>
- Syn:-
cat: To print file contents. (Read)cat:打印文件内容。(读取)- Syn:-
hdfs dfs -cat <path> - 语法:-
hdfs dfs -cat <路径>
- Syn:-
countcommand is used to count a number of directories, a number of files, and file size on HDFS.count命令用于计算HDFS上的目录数、文件数和文件大小。ducommand gives the size of each file in the directory.du命令给出目录中每个文件的大小。dusgives the total size of the directory/file.dus给出目录/文件的总大小。setRepcommand is used to change the replication factor of a file/directory in HDFSsetRep命令用于更改HDFS中文件/目录的副本因子touchz: It creates an empty file.touchz:它创建一个空文件。- test Options:
- 测试选项:
-e Checks if the file exists. Returns 0 if it exists.
-e 检查文件是否存在。如果存在则返回0。
-z Checks if the file is 0 bytes. If so, return 0.
-z 检查文件是否为0字节。如果是,则返回0。
-d If the path is a directory, return 1, otherwise return 0.
-d 如果路径是目录,则返回1,否则返回0。
hdfs dfs: check out the list of dfs commands using the following command.hdfs dfs:使用以下命令查看dfs命令列表。chmod:Change the permissions of fileschmod:更改文件权限chown:Change the owner of the fileschown:更改文件所有者hdfs dfs -stat <hdfs file>: It will give the last modified time of the directory or path.hdfs dfs -stat <hdfs文件>:它将给出目录或路径的最后修改时间。count:command is used to count a number of directories, a number of files, and file size on HDFS.count:命令用于计算HDFS上的目录数、文件数和文件大小。hdfs dfs -expunge:Clean up the recycle bin.hdfs dfs -expunge:清理回收站。
HDFS Read Architecture
HDFS读取架构
The client will reach out to
NameNodeasking for the block metadata for the file.客户端将联系
NameNode请求文件的块元数据。The
NameNodewill return the list ofDataNodes where each block (Block A and B) is stored.NameNode将返回存储每个块(块A和B)的DataNode列表。After that client, will connect to the
DataNodes where the blocks are stored.之后客户端将连接到存储块的
DataNode。The client starts reading data parallel from the
DataNodes (Block A fromDataNode1 and Block B fromDataNode3).客户端开始从
DataNode并行读取数据(从DataNode1读取块A,从DataNode3读取块B)。Once the client gets all the required file blocks, it will combine these blocks to form a file.
一旦客户端获得所有必需的文件块,它将组合这些块以形成文件。
HDFS Write Architecture
HDFS写入架构
To write data in HDFS, the client first interacts with the
NameNodeto get permission to write data and to get IPs ofDataNodes where the client writes the data.要在HDFS中写入数据,客户端首先与
NameNode交互以获得写入数据的权限,并获取客户端写入数据的DataNode的IP。The client then directly interacts with the
DataNodes for writing data.然后客户端直接与
DataNode交互以写入数据。The
DataNodethen creates a replica of the data block to otherDataNodes in the pipeline based on the replication factor.然后
DataNode根据副本因子在管道中为其他DataNode创建数据块的副本。If the replication factor is 3, then there will be a minimum of 3 copies of blocks created in different
DataNodes.如果副本因子为3,那么将在不同的
DataNode中创建至少3个块副本。
Java API methods for HDFS operation
HDFS操作的Java API方法
copyFromLocalFile: To upload a file from local machine to HDFS
copyFromLocalFile: 将文件从本地机器上传到HDFS
1
public void copyFromLocalFile(Path src, Path dst)
copyToLocalFile: To download a file from HDFS to local machine
copyToLocalFile:将文件从HDFS下载到本地机器
delete: Delete a file at the specified location
delete: 删除指定位置的文件
1
public abstract boolean delete(Path f, boolean recursive) throws IOException
rename: Rename a file at the specified location
rename: 重命名指定位置的文件
1
public abstract boolean rename(Path src, Path dst) throws IOException
mkdirs: Create a directory at the specified location
mkdirs: 在指定位置创建目录
1
public boolean mkdirs(Path f) throws IOException
listStatus: Display all directories and files in the current directory according to the given directory
listStatus: 根据给定目录显示当前目录中的所有目录和文件
1
public abstract FileStatus[] listStatus(Path f) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException
open: To open the file of HDFS FileSystem
open: 打开HDFS文件系统的文件
copyBytes: To copy data from input stream to output stream
copyBytes: 将数据从输入流复制到输出流
Java program to upload a file in HDFS
在HDFS中上传文件的Java程序
1 | public class CopyToHdfs { |
Java program to download a file from HDFS
从HDFS下载文件的Java程序
1 | public class CopyToLocal { |
Java program to rename a file in HDFS
在HDFS中重命名文件的Java程序
1 | public class RenameFile { |
Java program to delete a file in HDFS
在HDFS中删除文件的Java程序
1 | public class deleteFile { |
Chapter 5
- The MapReduce framework operates entirely on the basis of “key-value pairs,” in which data is entered as a batch of “key-value pairs,” and results are generated as a batch of “key-value pairs,” sometimes of different types.
- MapReduce框架完全基于”键值对”操作,其中数据以”键值对”批次输入,结果以”键值对”批次生成,有时是不同类型的。
- In Mapreduce, the output of Mapper will be the input of Reducer.
- 在MapReduce中,Mapper的输出将是Reducer的输入。
MapReduce Inputs and Outputs
MapReduce输入和输出
Input Files: The data for a MapReduce task is stored in input files, and input files typically lives in HDFS.
输入文件: MapReduce任务的数据存储在输入文件中,输入文件通常位于HDFS中。
InputFormat: The InputFormat processes the INPUT part of the MR to determine the number of maps.
InputFormat: InputFormat处理MR的输入部分以确定映射数量。
The InputFormat functions are as follows:
InputFormat的功能如下:
Verify that the input to the job is canonical.
验证作业的输入是规范的。
Cut the input file into InputSplit
将输入文件切分为InputSplit
Provides a RecordReader implementation class to read InputSplit into Mapper for processing
提供RecordReader实现类来读取InputSplit到Mapper进行处理
InputSplits: It is created by InputFormat, logically represent the data which will be processed by an individual Mapper
InputSplits: 它由InputFormat创建,逻辑上表示将由单个Mapper处理的数据
RecordReader: It communicates with the InputSplit in Hadoop MapReduce and converts the data into key-value pairs suitable for reading by the mapper.
RecordReader: 它在Hadoop MapReduce中与InputSplit通信,并将数据转换为适合映射器读取的键值对。
- By default, it uses TextInputFormat for converting data into a key-value pair.
- 默认情况下,它使用TextInputFormat将数据转换为键值对。
Mapper: It processes each input record (from RecordReader) and generates new key-value pair.
Mapper: 它处理每个输入记录(来自RecordReader)并生成新的键值对。
- The output of the Mapper (also known as intermediate output) is not stored on HDFS as this is temporary data and writing on HDFS will create unnecessary copies.
- Mapper的输出(也称为中间输出)不存储在HDFS上,因为这是临时数据,在HDFS上写入会创建不必要的副本。
- Combiner: The combiner is also known as ‘Mini-reducer’.
- Combiner: 组合器也被称为”迷你归约器”。
- Hadoop MapReduce Combiner performs local aggregation on the mappers’ output, which helps to minimize the data transfer between mapper and reducer.
- Hadoop MapReduce Combiner对映射器的输出执行本地聚合,这有助于最小化映射器和归约器之间的数据传输。
Partitioner: Partitioner comes into the picture if we are working on more than one reducer (for one reducer partitioner is not used).
Partitioner: 如果我们使用多个归约器,分区器就会发挥作用(对于一个归约器不使用分区器)。
Shuffling and Sorting: Once all the mappers are finished and their output is shuffled on the reducer nodes, then this intermediate output is merged and sorted, which is then provided as input to reduce phase
洗牌和排序: 一旦所有映射器完成并且它们的输出在归约器节点上洗牌,然后这个中间输出被合并和排序,然后作为输入提供给归约阶段
Reducer: It takes the set of intermediate key-value pairs produced by the mappers as the input and then runs a reduce function on each of them to generate the output.
Reducer: 它将映射器产生的中间键值对集合作为输入,然后在每个上运行归约函数以生成输出。
- The output of the reducer is the final output, which is stored in HDFS.
- 归约器的输出是最终输出,存储在HDFS中。
Map input type commonly used in Hadoop
Hadoop中常用的映射输入类型
TextInputFormat: TextInputFormat is the default input method of Hadoop.
TextInputFormat: TextInputFormat是Hadoop的默认输入方法。
- Each row of data generates a record, and each record is represented as <key,value>
- 每行数据生成一个记录,每个记录表示为<key,value>
SequenceFileInputFormat: Used to read sequence files.
SequenceFileInputFormat: 用于读取序列文件。
- Sequence files are binary files used by Hadoop to store data in a custom format .
- 序列文件是Hadoop用于以自定义格式存储数据的二进制文件。
KeyValueInputFormat: KeyValueInputFormat treats each line of the input file as a separate record and splits the line into key-value pairs by searching for TAB characters.
KeyValueInputFormat: KeyValueInputFormat将输入文件的每一行视为单独的记录,并通过搜索TAB字符将行分割为键值对。
Map output type commonly used in Hadoop
Hadoop中常用的映射输出类型
TextOutputFormat, output to a plain text file in the format of key + “\t” + value.
TextOutputFormat, 以key + “\t” + value的格式输出到纯文本文件。
NullOutputFormat, /dev/null in Hadoop, sends the output to the black hole.
NullOutputFormat, Hadoop中的/dev/null,将输出发送到黑洞。
SequenceFileOutputFormat, output to sequence file format files.
SequenceFileOutputFormat, 输出到序列文件格式文件。
MultipleSequenceFileOutputFormat, MultipleTextOutputFormat, according to the key records the output to a different file.
MultipleSequenceFileOutputFormat, MultipleTextOutputFormat,根据键将输出记录到不同的文件。
Key Processes of MapReduce
MapReduce的关键过程
Mapper: Mapper only understands <key, value> pairs of data, so before passing data to the mapper, data should be first converted into <key, value> pairs.
Mapper: Mapper只理解<key, value>数据对,所以在将数据传递给映射器之前,数据应该首先转换为<key, value>对。
a. InputSplits: It converts the physical representation of the block into logical for the Hadoop mapper.
a. InputSplits: 它将块的物理表示转换为Hadoop映射器的逻辑表示。b. RecordReader: The responsibility is to keep reading/converting data into key-value pairs until the end of the file.
b. RecordReader: 职责是持续读取/转换数据为键值对,直到文件结束。Partitioner: Partitioner needs to determine how to properly allocate Mapper output to the Reducer.
Partitioner: 分区器需要确定如何正确地将Mapper输出分配给Reducer。
Combiner: A combiner is equivalent to a local Reducer.
Combiner: 组合器相当于本地Reducer。
- It combines a large number of local files output by the Mapper to reduce data transfer between map and Reduce on the network.
- 它组合Mapper输出的大量本地文件,以减少网络上映射和归约之间的数据传输。
Reducer: Hadoop Reducer takes a set of intermediate key-value pairs produced by the mapper as the input and runs a Reducer function on each of them.
Reducer: Hadoop Reducer将映射器产生的中间键值对集合作为输入,并在每个上运行Reducer函数。
No of Mapper:
映射器数量:
- If we have a block size of 128 MB and we expect 10TB of input data, we will have 81920 maps.
- 如果我们有128MB的块大小,并且我们预期有10TB的输入数据,我们将有81920个映射。
- No of mapper = 10*1024*1024/ 128 = 81920
- 映射器数量 = 10*1024*1024/ 128 = 81920
Java Code of Mapper class (Wordcount program)
Mapper类的Java代码(单词计数程序)
1 | public class wordcountmapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> { |
Java Code for Reducer class (Wordcount program)
Reducer类的Java代码(单词计数程序)
1 | public class wordcountreducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> { |
Introduction to Job Scheduler
作业调度器介绍
The default scheduler FIFO: First In First Out (FIFO) algorithm for job scheduling.
默认调度器FIFO: 作业调度的先进先出(FIFO)算法。
Disadvantages
缺点
Ignoring differences in the requirements of different jobs
忽略不同作业需求的差异
Computing Capacity Scheduler: In Capacity Scheduler we have multiple job queues for scheduling our tasks means allows multiple occupants to share a large size Hadoop cluster
计算能力调度器: 在能力调度器中,我们有多个作业队列来调度我们的任务,这意味着允许多个占用者共享大型Hadoop集群
Disadvantages:
缺点:
More complex
更复杂
Not easy to configure for everyone
不是每个人都容易配置
Fair Scheduler: The Fair Scheduler is very much similar to the capacity scheduler.
公平调度器: 公平调度器与能力调度器非常相似。
The priority of the job is kept in consideration.
- 作业的优先级被考虑在内。
Disadvantages:
缺点:
The configuration is required.
需要配置。
Chapter 6
Serialization is the name given to the process that converts any object state or data into a series of bits which it can easily store in memory or file formats.
序列化是将任何对象状态或数据转换为可以轻松存储在内存或文件格式中的位系列的过程的名称。
DataOutputStream class is used to implement Hadoop serialization while ObjectOutputStream is used to implement Java serialization.
DataOutputStream类用于实现Hadoop序列化,而ObjectOutputStream用于实现Java序列化。
Data Serialization in Hadoop
Hadoop中的数据序列化
- Serialization and deserialization in Hadoop are done via the Writable interface.
- Hadoop中的序列化和反序列化通过Writable接口完成。
- This interface has two methods, void write (DataOutput out) and void readFields (DataInput in).
- 该接口有两个方法,void write (DataOutput out)和void readFields (DataInput in)。
Why use Hadoop serialization over java serialization?
为什么使用Hadoop序列化而不是Java序列化?
- The serialized value using Java serialization is way bigger than the serialized values of a Writable class
- 使用Java序列化的序列化值比Writable类的序列化值大得多
Compression Formats
压缩格式
gzip: gzip is naturally supported by Hadoop.
gzip:gzip自然支持Hadoop。
Class name : org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GZipCodec
类名:org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GZipCodecLZO: it decompresses about twice as fast as gzip
LZO:它的解压缩速度大约是gzip的两倍
Class name: com.hadoop.compression.lzo.LzopCodec
类名:com.hadoop.compression.lzo.LzopCodecSnappy: It is a compression/decompression library.
Snappy:它是一个压缩/解压缩库。
Class name: org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec
类名:org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodecbzip2: It is a freely available, patent free, high-quality data compressor.
bzip2:它是一个免费可用的、无专利的高质量数据压缩器。
Class name: org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.BZip2Codec
类名:org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.BZip2Codec
Java program to compress a file
压缩文件的Java程序
1 | public class Compress { |
Java program to decompress a file
解压缩文件的Java程序
1 | public class Decompress { |
The classes used for file compression and decompression:
用于文件压缩和解压缩的类:
CompressionCodecFactory
CompressionCodec
CompressionOutputStream
Java program to compress a file using Bzip2 format
使用Bzip2格式压缩文件的Java程序
1 | public class FileCompress { |
- Hadoop’s HDFS and MapReduce sub-frameworks are mainly designed for large data files, which are not only inefficient in processing small files, but also consume a lot of disk space (each small file occupies a Block, the default size of HDFS block is 128M).
- Hadoop的HDFS和MapReduce子框架主要为大数据文件设计,它们在处理小文件方面不仅效率低,而且消耗大量磁盘空间(每个小文件占用一个块,HDFS块的默认大小是128M)。
SequenceFile Container Class
SequenceFile容器类
SequenceFile is a binary file support provided by Hadoop API.
SequenceFile是Hadoop API提供的二进制文件支持。
This binary file serializes <key, value> pairs directly into the file.
这个二进制文件直接将<key, value>对序列化到文件中。
Their basic idea is to merge small files into a large file.
它们的基本思想是将小文件合并为大文件。
Compression of Sequence File
序列文件的压缩
The Sequence File can support three compression types:
序列文件可以支持三种压缩类型:
NONE: Records are not compressed.
NONE: 记录不被压缩。
RECORD: Compress only the value in each record;
RECORD: 仅压缩每个记录中的值;
BLOCK: Compress all records in a block;
BLOCK: 压缩块中的所有记录;
Structure of Sequence File
序列文件的结构
A sequence is built up of Records.
序列由记录构成。
Each record is a combination of key, value pairs.
每个记录是键值对的组合。
Inside each record it has Record Length, Key Length, Key and Value.
在每个记录内部,它有记录长度、键长度、键和值。
Inside each record it has Record Length, Key Length, Key and Compressed Value in record level compression.
在记录级压缩中,每个记录内部有记录长度、键长度、键和压缩值。
Each block in block level compressed sequence file will contain number of records, which is uncompressed, compressed key lengths, compressed keys, compressed value lengths and actual values compressed.
块级压缩序列文件中的每个块将包含记录数量(未压缩)、压缩键长度、压缩键、压缩值长度和实际压缩值。
MapFile Class
MapFile类
MapFile files can be seen as SequenceFile files that store ordered key-value.
MapFile文件可以看作是存储有序键值的SequenceFile文件。
MapFile files ensure that key-value keys are ordered (key-based).
MapFile文件确保键值的键是有序的(基于键)。
Chapter 7
- MapReduce’s design pattern is a template that uses MapReduce to solve conventional data processing problems.
- MapReduce的设计模式是使用MapReduce解决传统数据处理问题的模板。
- It’s just a general way of dealing with problems.
- 这只是处理问题的一般方法。
- The design patterns are the solution templates for solving specific problems
- 设计模式是解决特定问题的解决方案模板
Why MapReduce Design Patterns:
为什么要使用MapReduce设计模式:
Map Reduce framework does provide techniques for controlling execution and managing the flow of data.
MapReduce框架确实提供了控制执行和管理数据流的技术。
Ability to construct complex data structures as key/value.
能够构造复杂的数据结构作为键/值。
To store and communicate partial results-specified field initialization & termination code at the start/end of map-reduce jobs.
存储和通信部分结果——在map-reduce作业开始/结束时指定字段初始化和终止代码。
Ability to preserve state in mappers and reducers across multiple input or intermediate keys.
能够在映射器和归约器中跨多个输入或中间键保持状态。
Ability to control the sort order of intermediate keys, therefore order in which reducers will encounter particular keys.
能够控制中间键的排序顺序,因此控制归约器遇到特定键的顺序。
Ability to control the partitioning of the key space therefore set of keys to be sent to a particular reducer.
能够控制键空间的分区,因此控制要发送到特定归约器的键集。
Mapreduce Design pattern
MapReduce设计模式
Summarization patterns
汇总模式
It’s all about grouping similar data together and then performing an operation such as calculating a minimum, maximum, count, average
这完全是关于将相似的数据分组在一起,然后执行诸如计算最小值、最大值、计数、平均值等操作Filter Pattern
过滤模式
simply filtering out records based on a particular condition.
简单地根据特定条件过滤记录。Top N Design Pattern
Top N设计模式
When the intent is to find the top-ranking data.
当意图是找到排名靠前的数据时。Distinct Pattern
去重模式
When the intent is to remove all duplicates then this pattern applies.
当意图是删除所有重复项时,应用此模式。Data Organization Pattern
数据组织模式
Data reorganization refers to the reorganization of data according to certain rules, such as a group of men, a group of women, and a group of unknown gender.
数据重组是指根据某些规则重新组织数据,例如一组男性、一组女性和一组未知性别。Join Pattern
连接模式
Implement data association and combination of multiple data sources.
实现数据关联和多个数据源的组合。
Chapter 8
- Remote Procedure calls allow one computer program to Call subroutines of another computer remotely, without worrying about the underlying network communication details.
- 远程过程调用允许一个计算机程序远程调用另一个计算机的子程序,而无需担心底层网络通信细节。
Hadoop RPC Communication
Hadoop RPC通信
Serialization Layer
序列化层
Function Call Layer
函数调用层
Network Transport Layer
网络传输层
Server-side Framework Layer
服务器端框架层
Hadoop RPC Design Technique
Hadoop RPC设计技术
Dynamic Agent
动态代理
Reflection.
反射。
Serialization.
序列化。
Non-blocking asynchronous IO (NIO)
非阻塞异步IO(NIO)
Hadoop RPC Usage Method
Hadoop RPC使用方法
using Hadoop RPC can be divided into the following 4 steps:
使用Hadoop RPC可以分为以下4个步骤:
RPC protocol Definition
RPC协议定义
RPC protocol is the communication interface between client and server.
RPC协议是客户端和服务器之间的通信接口。Implementing RPC Protocol
实现RPC协议
Construction and start-up of RPC Server
RPC服务器的构建和启动
Construct RPC Client and send RPC request
构造RPC客户端并发送RPC请求
Configuration for file optimization
文件优化配置
| Property | Default Value | Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| 属性 | 默认值 | 优化 |
| dfs.block.size | 128MB | Can be changed to 256 MB by changing it to bytes. |
| dfs.block.size | 128MB | 可以通过将其更改为字节来更改为256MB。 |
HAR Syntax
HAR语法
Archive all small files under a directory /NIIT/data into /NIIT/outputdir /data.har:
将目录/NIIT/data下的所有小文件归档到/NIIT/outputdir /data.har:
1
hadoop archive -archiveName data.har -p /niit/data /niit/outputdir/
View the files in the HAR file archive as follows:
查看HAR文件归档中的文件如下:
1
hdfs dfs -ls har:///niit/data/data.har