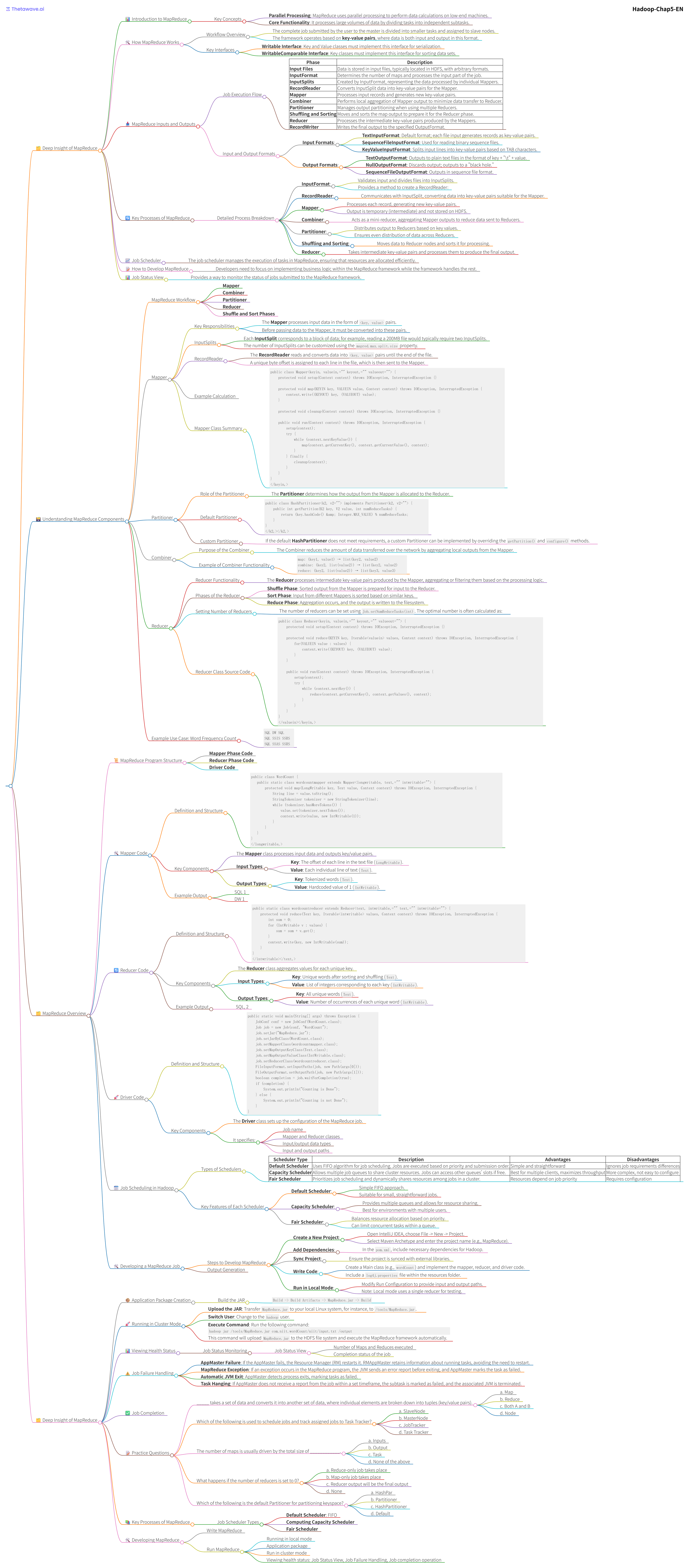
🗂️ Deep Insight of MapReduce
🗂️ MapReduce 深入解析
📊 Introduction to MapReduce
📊 MapReduce 简介
“The MapReduce programming model is one of the core modules of Hadoop that runs in the background of Hadoop to provide scalability and easy data-processing solutions.”
“MapReduce 编程模型是 Hadoop 的核心模块之一,它在 Hadoop 后台运行,以提供可扩展性和简单的数据处理解决方案。”
Key Concepts
核心概念
- Parallel Processing: MapReduce uses parallel processing to perform data calculations on low-end machines.
- 并行处理:MapReduce 使用并行处理在低端机器上执行数据计算。
- Core Functionality: It processes large volumes of data by dividing tasks into independent subtasks.
- 核心功能:它通过将任务划分为独立的子任务来处理大量数据。
🛠️ How MapReduce Works
🛠️ MapReduce 工作原理
Workflow Overview
工作流程概述
- The complete job submitted by the user to the master is divided into smaller tasks and assigned to slave nodes.
- 用户提交给主节点的完整作业被划分为更小的任务并分配给从节点。
- The framework operates based on key-value pairs, where data is both input and output in this format.
- 该框架基于键值对运行,其中数据以此格式输入和输出。
Key Interfaces
关键接口
- Writable Interface: Key and Value classes must implement this interface for serialization.
- Writable 接口:键和值类必须实现此接口以进行序列化。
- WritableComparable Interface: Key classes must implement this interface for sorting data sets.
- WritableComparable 接口:键类必须实现此接口以对数据集进行排序。
📥 MapReduce Inputs and Outputs
📥 MapReduce 输入与输出
Job Execution Flow
作业执行流程
The execution of a MapReduce job consists of several phases:
MapReduce 作业的执行包括几个阶段:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| 阶段 | 描述 |
| Input Files | Data is stored in input files, typically located in HDFS, with arbitrary formats. |
| 输入文件 | 数据存储在输入文件中,通常位于 HDFS 中,格式任意。 |
| InputFormat | Determines the number of maps and processes the input part of the job. |
| InputFormat (输入格式) | 决定 map 的数量并处理作业的输入部分。 |
| InputSplits | Created by InputFormat, representing the data processed by individual Mappers. |
| InputSplits (输入分片) | 由 InputFormat 创建,表示由各个 Mapper 处理的数据。 |
| RecordReader | Converts InputSplit data into key-value pairs for the Mapper. |
| RecordReader (记录读取器) | 将 InputSplit 数据转换为键值对以供 Mapper 使用。 |
| Mapper | Processes input records and generates new key-value pairs. |
| Mapper (映射器) | 处理输入记录并生成新的键值对。 |
| Combiner | Performs local aggregation of Mapper output to minimize data transfer to Reducer. |
| Combiner (合并器) | 执行 Mapper 输出的本地聚合,以最大限度地减少传输到 Reducer 的数据。 |
| Partitioner | Manages output partitioning when using multiple Reducers. |
| Partitioner (分区器) | 在使用多个 Reducer 时管理输出分区。 |
| Shuffling and Sorting | Moves and sorts the map output to prepare it for the Reducer phase. |
| Shuffling and Sorting (混洗和排序) | 移动并排序 map 输出,为 Reducer 阶段做准备。 |
| Reducer | Processes the intermediate key-value pairs produced by the Mappers. |
| Reducer (化简器) | 处理由 Mapper 生成的中间键值对。 |
| RecordWriter | Writes the final output to the specified OutputFormat. |
| RecordWriter (记录写入器) | 将最终输出写入指定的 OutputFormat。 |
Input and Output Formats
输入和输出格式
- Input Formats:
- 输入格式:
- TextInputFormat: Default format; each file input generates records as key-value pairs.
- TextInputFormat:默认格式;每个文件输入都以键值对的形式生成记录。
- SequenceFileInputFormat: Used for reading binary sequence files.
- SequenceFileInputFormat:用于读取二进制序列文件。
- KeyValueInputFormat: Splits input lines into key-value pairs based on TAB characters.
- KeyValueInputFormat:根据 TAB 字符将输入行拆分为键值对。
- Output Formats:
- 输出格式:
- TextOutputFormat: Outputs to plain text files in the format of key + “\t” + value.
- TextOutputFormat:以键 + “\t” + 值的格式输出到纯文本文件。
- NullOutputFormat: Discards output; outputs to a “black hole.”
- NullOutputFormat:丢弃输出;输出到“黑洞”。
- SequenceFileOutputFormat: Outputs in sequence file format.
- SequenceFileOutputFormat:以序列文件格式输出。
🔄 Key Processes of MapReduce
🔄 MapReduce 的关键流程
Detailed Process Breakdown
详细流程分解
InputFormat:
- Validates input and divides files into InputSplits.
- Provides a method to create a RecordReader:
1
public abstract RecordReader<K,V> createRecordReader(InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException;
InputFormat (输入格式):
- 验证输入并将文件划分为 InputSplits。
- 提供创建 RecordReader 的方法:
1
public abstract RecordReader<K,V> createRecordReader(InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException;
RecordReader:
- Communicates with InputSplit, converting data into key-value pairs suitable for the Mapper.
RecordReader (记录读取器):
- 与 InputSplit 通信,将数据转换为适合 Mapper 的键值对。
Mapper:
- Processes each record, generating new key-value pairs.
- Output is temporary (intermediate) and not stored on HDFS.
Mapper (映射器):
- 处理每个记录,生成新的键值对。
- 输出是临时的(中间的),不存储在 HDFS 上。
Combiner:
- Acts as a mini-reducer, aggregating Mapper outputs to reduce data sent to Reducers.
Combiner (合并器):
- 充当迷你化简器,聚合 Mapper 输出以减少发送到 Reducer 的数据。
Partitioner:
- Distributes output to Reducers based on key values.
- Ensures even distribution of data across Reducers.
Partitioner (分区器):
- 根据键值将输出分配给 Reducer。
- 确保数据在 Reducer 之间均匀分布。
Shuffling and Sorting:
- Moves data to Reducer nodes and sorts it for processing.
Shuffling and Sorting (混洗和排序):
- 将数据移动到 Reducer 节点并对其进行排序以进行处理。
Reducer:
- Takes intermediate key-value pairs and processes them to produce the final output.
Reducer (化简器):
- 获取中间键值对并对其进行处理以生成最终输出。
📈 Job Scheduler
📈 作业调度器
- The job scheduler manages the execution of tasks in MapReduce, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
- 作业调度器管理 MapReduce 中任务的执行,确保资源得到有效分配。
📝 How to Develop MapReduce
📝 如何开发 MapReduce
- Developers need to focus on implementing business logic within the MapReduce framework while the framework handles the rest.
- 开发人员需要专注于在 MapReduce 框架内实现业务逻辑,而框架则处理其余部分。
📊 Job Status View
📊 作业状态视图
- Provides a way to monitor the status of jobs submitted to the MapReduce framework.
- 提供一种监控提交到 MapReduce 框架的作业状态的方法。
🗃️ Understanding MapReduce Components
🗃️ 理解 MapReduce 组件
MapReduce Workflow
MapReduce 工作流程
MapReduce is a programming model for processing large data sets with a distributed algorithm on a cluster. The core components involved in this workflow are:
MapReduce 是一种用于在集群上使用分布式算法处理大型数据集的编程模型。此工作流程中涉及的核心组件包括:
- Mapper
- Mapper (映射器)
- Combiner
- Combiner (合并器)
- Partitioner
- Partitioner (分区器)
- Reducer
- Reducer (化简器)
- Shuffle and Sort Phases
- Shuffle and Sort Phases (混洗和排序阶段)
Mapper
Mapper (映射器)
Key Responsibilities
主要职责
- The Mapper processes input data in the form of
<key, value>pairs. - Mapper 以
<键, 值>对的形式处理输入数据。 - Before passing data to the Mapper, it must be converted into these pairs.
- 在将数据传递给 Mapper 之前,必须将其转换为这些键值对。
InputSplits
InputSplits (输入分片)
“InputSplits convert the physical representation of the block into logical representations for the Hadoop mapper.”
“InputSplits 将块的物理表示形式转换为 Hadoop 映射器的逻辑表示形式。”
- Each InputSplit corresponds to a block of data; for example, reading a 200MB file would typically require two InputSplits.
- 每个 InputSplit 对应一个数据块;例如,读取一个 200MB 的文件通常需要两个 InputSplits。
- The number of InputSplits can be customized using the
mapred.max.split.sizeproperty. - 可以使用
mapred.max.split.size属性自定义 InputSplits 的数量。
RecordReader
RecordReader (记录读取器)
- The RecordReader reads and converts data into
<key, value>pairs until the end of the file. - RecordReader 读取数据并将其转换为
<键, 值>对,直到文件末尾。 - A unique byte offset is assigned to each line in the file, which is then sent to the Mapper.
- 文件中的每一行都被分配一个唯一的字节偏移量,然后将其发送给 Mapper。
Example Calculation
计算示例
If you have a block size of 128 MB and expect 10 TB of input data, the number of Mappers can be calculated as:
如果您的块大小为 128 MB,并且预计输入数据为 10 TB,则 Mapper 的数量可以计算如下:
Number of Mappers=Input Split SizeTotal Data Size
Mapper 数量=输入分片大小总数据大小
For example, if the data size is 1 TB and InputSplit size is 200 MB:
例如,如果数据大小为 1 TB,输入分片大小为 200 MB:
Number of Mappers=2001000×1000=5000
Mapper 数量=2001000×1000=5000
Mapper Class Summary
Mapper 类摘要
1 | public class Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> { |
Partitioner
Partitioner (分区器)
Role of the Partitioner
分区器的角色
- The Partitioner determines how the output from the Mapper is allocated to the Reducer.
- Partitioner 决定如何将 Mapper 的输出分配给 Reducer。
Default Partitioner
默认分区器
- By default, Hadoop uses a HashPartitioner:
- 默认情况下,Hadoop 使用 HashPartitioner:
1 | public class HashPartitioner<K2, V2> implements Partitioner<K2, V2> { |
Custom Partitioner
自定义分区器
- If the default HashPartitioner does not meet requirements, a custom Partitioner can be implemented by overriding the
getPartition()andconfigure()methods. - 如果默认的 HashPartitioner 不符合要求,可以通过覆盖
getPartition()和configure()方法来实现自定义 Partitioner。
Combiner
Combiner (合并器)
Purpose of the Combiner
合并器的目的
“A Combiner is equivalent to a local Reducer that aggregates data before sending it to the Reducer to reduce data transfer.”
“Combiner 相当于一个本地 Reducer,它在将数据发送到 Reducer 之前对其进行聚合,以减少数据传输。”
- The Combiner reduces the amount of data transferred over the network by aggregating local outputs from the Mapper.
- Combiner 通过聚合 Mapper 的本地输出来减少通过网络传输的数据量。
Example of Combiner Functionality
合并器功能示例
- Input and output flow:
- 输入输出流程:
1 | map: (key1, value1) → list(key2, value2) |
Reducer
Reducer (化简器)
Reducer Functionality
化简器功能
- The Reducer processes intermediate key-value pairs produced by the Mapper, aggregating or filtering them based on the processing logic.
- Reducer 处理由 Mapper 生成的中间键值对,并根据处理逻辑对其进行聚合或筛选。
Phases of the Reducer
化简器的阶段
- Shuffle Phase: Sorted output from the Mapper is prepared for input to the Reducer.
- Shuffle Phase (混洗阶段):将来自 Mapper 的已排序输出准备好作为 Reducer 的输入。
- Sort Phase: Input from different Mappers is sorted based on similar keys.
- Sort Phase (排序阶段):来自不同 Mapper 的输入根据相似的键进行排序。
- Reduce Phase: Aggregation occurs, and the output is written to the filesystem.
- Reduce Phase (化简阶段):进行聚合,并将输出写入文件系统。
Setting Number of Reducers
设置 Reducer 数量
- The number of reducers can be set using
Job.setNumReduceTasks(int). The optimal number is often calculated as: - 可以使用
Job.setNumReduceTasks(int)设置 reducer 的数量。最佳数量通常计算如下:
Optimal Reducers=0.95 or 1.75×(no. of nodes×max containers per node)
最佳 Reducer 数量=0.95 或 1.75×(节点数×每个节点的最大容器数)
Reducer Class Source Code
Reducer 类源代码
1 | public class Reducer<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> { |
Example Use Case: Word Frequency Count
示例用例:词频统计
A practical example of a MapReduce job is counting the occurrences of each word in a given text, such as:
MapReduce 作业的一个实际示例是统计给定文本中每个单词出现的次数,例如:
1 | SQL DW SQL |
This input can be processed using the aforementioned components to yield the frequency of each word.
可以使用上述组件处理此输入,以产生每个单词的频率。
🗂️ MapReduce Overview
🗂️ MapReduce 概述
📜 MapReduce Program Structure
📜 MapReduce 程序结构
The MapReduce program can be fundamentally divided into three main parts:
MapReduce 程序基本上可以分为三个主要部分:
- Mapper Phase Code
- Mapper Phase Code (Mapper 阶段代码)
- Reducer Phase Code
- Reducer Phase Code (Reducer 阶段代码)
- Driver Code
- Driver Code (驱动程序代码)
We will explore the code for each of these sections in detail.
我们将详细探讨这些部分中的每一部分的代码。
🛠️ Mapper Code
🛠️ Mapper 代码
Definition and Structure
定义和结构
1 | public class WordCount { // WordCount 类 |
Key Components
关键组件
- The Mapper class processes input data and outputs key/value pairs.
- Mapper 类处理输入数据并输出键/值对。
- Input Types:
- Key: The offset of each line in the text file (
LongWritable). - Value: Each individual line of text (
Text).
- Key: The offset of each line in the text file (
- 输入类型:
- 键:文本文件中每行的偏移量 (
LongWritable)。 - 值:每行单独的文本 (
Text)。
- 键:文本文件中每行的偏移量 (
- Output Types:
- Key: Tokenized words (
Text). - Value: Hardcoded value of 1 (
IntWritable).
- Key: Tokenized words (
- 输出类型:
- 键:分词后的单词 (
Text)。 - 值:硬编码的值 1 (
IntWritable)。
- 键:分词后的单词 (
Example Output
输出示例
For input like “SQL” or “DW”, the output would be:
对于像 “SQL” 或 “DW” 这样的输入,输出将是:
- SQL 1
- DW 1
🔄 Reducer Code
🔄 Reducer 代码
Definition and Structure
定义和结构
1 | public static class wordcountreducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> { // wordcountreducer 类继承自 Reducer |
Key Components
关键组件
- The Reducer class aggregates values for each unique key.
- Reducer 类对每个唯一键的值进行聚合。
- Input Types:
- Key: Unique words after sorting and shuffling (
Text). - Value: List of integers corresponding to each key (
IntWritable).
- Key: Unique words after sorting and shuffling (
- 输入类型:
- 键:排序和混洗后的唯一单词 (
Text)。 - 值:与每个键对应的整数列表 (
IntWritable)。
- 键:排序和混洗后的唯一单词 (
- Output Types:
- Key: All unique words (
Text). - Value: Number of occurrences of each unique word (
IntWritable).
- Key: All unique words (
- 输出类型:
- 键:所有唯一的单词 (
Text)。 - 值:每个唯一单词出现的次数 (
IntWritable)。
- 键:所有唯一的单词 (
Example Output
输出示例
For input “SQL, [1, 1]”, the output would be:
对于输入 “SQL, [1, 1]”,输出将是:
- SQL, 2
🚀 Driver Code
🚀 驱动程序代码
Definition and Structure
定义和结构
1 | public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 主方法 |
Key Components
关键组件
- The Driver class sets up the configuration of the MapReduce job.
- Driver 类设置 MapReduce 作业的配置。
- It specifies:
- Job name
- Mapper and Reducer classes
- Input/output data types
- Input and output paths
- 它指定:
- 作业名称
- Mapper 和 Reducer 类
- 输入/输出数据类型
- 输入和输出路径
🗓️ Job Scheduling in Hadoop
🗓️ Hadoop 中的作业调度
Types of Schedulers
调度器类型
| Scheduler Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| 调度器类型 | 描述 | 优点 | 缺点 |
| Default Scheduler | Uses FIFO algorithm for job scheduling. Jobs are executed based on priority and submission order. | Simple and straightforward | Ignores job requirements differences |
| 默认调度器 | 使用 FIFO 算法进行作业调度。作业根据优先级和提交顺序执行。 | 简单直接 | 忽略作业需求差异 |
| Capacity Scheduler | Allows multiple job queues to share cluster resources. Jobs can access other queues’ slots if free. | Best for multiple clients, maximizes throughput | More complex, not easy to configure |
| 容量调度器 | 允许多个作业队列共享集群资源。如果其他队列的槽位空闲,作业可以访问它们。 | 最适合多客户端,最大化吞吐量 | 更复杂,不易配置 |
| Fair Scheduler | Prioritizes job scheduling and dynamically shares resources among jobs in a cluster. | Resources depend on job priority | Requires configuration |
| 公平调度器 | 优先作业调度,并在集群中的作业之间动态共享资源。 | 资源取决于作业优先级 | 需要配置 |
Key Features of Each Scheduler
各调度器的主要特点
- Default Scheduler:
- Simple FIFO approach.
- Suitable for small, straightforward jobs.
- 默认调度器:
- 简单的 FIFO 方法。
- 适用于小型、简单的作业。
- Capacity Scheduler:
- Provides multiple queues and allows for resource sharing.
- Best for environments with multiple users.
- 容量调度器:
- 提供多个队列并允许资源共享。
- 最适合多用户环境。
- Fair Scheduler:
- Balances resource allocation based on priority.
- Can limit concurrent tasks within a queue.
- 公平调度器:
- 根据优先级平衡资源分配。
- 可以在队列内限制并发任务。
🛠️ Developing a MapReduce Job
🛠️ 开发 MapReduce 作业
Steps to Develop MapReduce
开发 MapReduce 的步骤
- Create a New Project:
- Open IntelliJ IDEA, choose File -> New -> Project.
- Select Maven Archetype and enter the project name (e.g., MapReduce).
- 创建新项目:
- 打开 IntelliJ IDEA,选择文件 -> 新建 -> 项目。
- 选择 Maven Archetype 并输入项目名称(例如,MapReduce)。
- Add Dependencies:
- In the
pom.xml, include necessary dependencies for Hadoop.
- In the
- 添加依赖项:
- 在
pom.xml中,包含 Hadoop 所需的依赖项。
- 在
- Sync Project:
- Ensure the project is synced with external libraries.
- 同步项目:
- 确保项目与外部库同步。
- Write Code:
- Create a Main class (e.g.,
wordCount) and implement the mapper, reducer, and driver code. - Include a
log4j.propertiesfile within the resources folder.
- Create a Main class (e.g.,
- 编写代码:
- 创建一个主类(例如,
wordCount)并实现 mapper、reducer 和驱动程序代码。 - 在 resources 文件夹中包含一个
log4j.properties文件。
- 创建一个主类(例如,
- Run in Local Mode:
- Modify Run Configuration to provide input and output paths.
- Note: Local mode uses a single reducer for testing.
- 在本地模式下运行:
- 修改运行配置以提供输入和输出路径。
- 注意:本地模式使用单个 reducer 进行测试。
Output Generation
输出生成
Upon executing the MapReduce job, the specified output files will be generated in the designated output directory.
执行 MapReduce 作业后,指定的输出文件将在指定的输出目录中生成。
🗂️ Deep Insight of MapReduce
🗂️ MapReduce 深入解析
📦 Application Package Creation
📦 应用程序包创建
To create a JAR package in your project, follow these steps:
要在项目中创建 JAR 包,请执行以下步骤:
- Select the Main Class: Go to
File -> Project Structure -> Artifacts -> JAR, and from there, select the Main class from your project. - 选择主类:转到
文件 -> 项目结构 -> 构建 -> JAR,然后从项目中选择主类。 - Output Directory: Choose the Output directory where your final JAR file will be stored. For this example, set it to
src/main/resources. - 输出目录:选择最终 JAR 文件将存储的输出目录。对于此示例,将其设置为
src/main/resources。 - Export the JAR: Click OK to export the JAR package, then select Apply and OK.
- 导出 JAR:单击确定以导出 JAR 包,然后选择应用和确定。
Build the JAR
构建 JAR
To finalize your JAR file, navigate to:
要完成 JAR 文件,请导航至:
Build -> Build Artifacts -> MapReduce.jar -> Build构建 -> 构建工件 -> MapReduce.jar -> 构建
After building, you will find the JAR file in the resources folder of your project.
构建后,您将在项目的 resources 文件夹中找到 JAR 文件。
🚀 Running in Cluster Mode
🚀 在集群模式下运行
To run your MapReduce application in cluster mode:
要在集群模式下运行 MapReduce 应用程序:
Upload the JAR: Transfer
MapReduce.jarto your local Linux system, for instance, to/tools/MapReduce.jar.上传 JAR:将
MapReduce.jar传输到本地 Linux 系统,例如,传输到/tools/MapReduce.jar。Switch User: Change to the
hadoopuser.切换用户:切换到
hadoop用户。Execute Command:
Run the following command:
1
hadoop jar /tools/MapReduce.jar com.niit.wordCount/niit/input.txt /output
This command will upload
1
MapReduce.jar
to the HDFS file system and execute the MapReduce framework automatically.
执行命令:
运行以下命令:
1
hadoop jar /tools/MapReduce.jar com.niit.wordCount/niit/input.txt /output
此命令会将
1
MapReduce.jar
上传到 HDFS 文件系统并自动执行 MapReduce 框架。
📊 Viewing Health Status
📊 查看健康状况
To monitor the health status of your MapReduce jobs:
要监控 MapReduce 作业的健康状况:
- Enter the following URL in your browser:
http://niit:8088to access the resource manager state, which displays the running MapReduce programs. - 在浏览器中输入以下 URL:
http://niit:8088以访问资源管理器状态,该状态显示正在运行的 MapReduce 程序。
Job Status Monitoring
作业状态监控
When a job is active, the Resource Manager can be used to view the current running status:
当作业处于活动状态时,可以使用资源管理器查看当前的运行状态:
- AppMaster: Periodically reports the status of tasks, such as the number of Map and Reduce tasks, and their overall running status.
- AppMaster:定期报告任务的状态,例如 Map 和 Reduce 任务的数量及其总体运行状态。
Job Status View
作业状态视图
Click on ApplicationMaster to see the execution status of the job, including:
单击 ApplicationMaster 查看作业的执行状态,包括:
- Number of Maps and Reduces executed
- 已执行的 Map 和 Reduce 数量
- Completion status of the job
- 作业的完成状态
⚠️ Job Failure Handling
⚠️ 作业失败处理
Various job failure scenarios are managed by the YARN model:
YARN 模型管理各种作业失败场景:
- AppMaster Failure: If the AppMaster fails, the Resource Manager (RM) restarts it. RMAppMaster retains information about running tasks, avoiding the need to restart.
- AppMaster 失败:如果 AppMaster 失败,资源管理器 (RM) 会重新启动它。RMAppMaster 保留有关正在运行的任务的信息,从而避免了重新启动的需要。
- MapReduce Exception: If an exception occurs in the MapReduce program, the JVM sends an error report before exiting, and AppMaster marks the task as failed.
- MapReduce 异常:如果在 MapReduce 程序中发生异常,JVM 会在退出前发送错误报告,AppMaster 会将该任务标记为失败。
- Automatic JVM Exit: AppMaster detects process exits, marking tasks as failed.
- JVM 自动退出:AppMaster 检测到进程退出,并将任务标记为失败。
- Task Hanging: If AppMaster does not receive a report from the job within a set timeframe, the subtask is marked as failed, and the associated JVM is terminated.
- 任务挂起:如果 AppMaster 在设定的时间范围内未收到作业的报告,则该子任务将被标记为失败,并且关联的 JVM 将被终止。
After a job failure, AppMaster will request resources to restart the task. If errors exceed a certain threshold, the task will not be retried.
作业失败后,AppMaster 将请求资源以重新启动任务。如果错误超过某个阈值,则不会重试该任务。
✅ Job Completion
✅ 作业完成
After the application has run successfully, ApplicationMaster logs out from ResourceManager and closes itself, marking the job as complete.
应用程序成功运行后,ApplicationMaster 从 ResourceManager 注销并自行关闭,将作业标记为完成。
📚 Key Processes of MapReduce
📚 MapReduce 的关键流程
- Mapper
- Mapper (映射器)
- Partitioner
- Partitioner (分区器)
- Combiner
- Combiner (合并器)
- Reducer
- Reducer (化简器)
Job Scheduler Types
作业调度器类型
- Default Scheduler: FIFO
- 默认调度器:FIFO
- Computing Capacity Scheduler
- 计算能力调度器
- Fair Scheduler
- 公平调度器
🛠️ Developing MapReduce
🛠️ 开发 MapReduce
- Write MapReduce
- 编写 MapReduce
- Run MapReduce
- 运行 MapReduce
- Running in local mode
- 在本地模式下运行
- Application package
- 应用程序包
- Run in cluster mode
- 在集群模式下运行
- Viewing health status: Job Status View, Job Failure Handling, Job completion operation
- 查看健康状况:作业状态视图、作业失败处理、作业完成操作
🤔思维导图